Exploración de las baterías del sistema UPS: roles y funciones esenciales
Tabla de contenido
Welcome to the world of Uninterruptible Power Supply, or UPS, systems! If you’ve ever wondered about how the gadgets and devices in hospitals, data centers, and even your home office keep running smoothly during a power outage, you’re about to find out. Today, we’re diving into the essential roles and functions of UPS batteries, which play a crucial role in our digital and medical infrastructures.First off, let's clear up some basics. When we talk about a UPS, we're referring to a system designed to keep electronic devices powered in the event of a power outage. So, what is a UPS unit? Simply put, it’s a device that instantly switches to battery power when it detects that the main power has been interrupted. This transition happens so quickly that the devices connected to the UPS don’t even notice the switch – they keep running without a hiccup!Now, you might be asking, "What does UPS battery mean?" or "Define UPS." A UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, is essentially a guard against power interruptions. It combines a battery and a few other components to make sure your essential gadgets and machines don’t turn off unexpectedly. This is super important in places like hospitals, where equipment needs to be on all the time.Let’s break down the main parts of a UPS system:
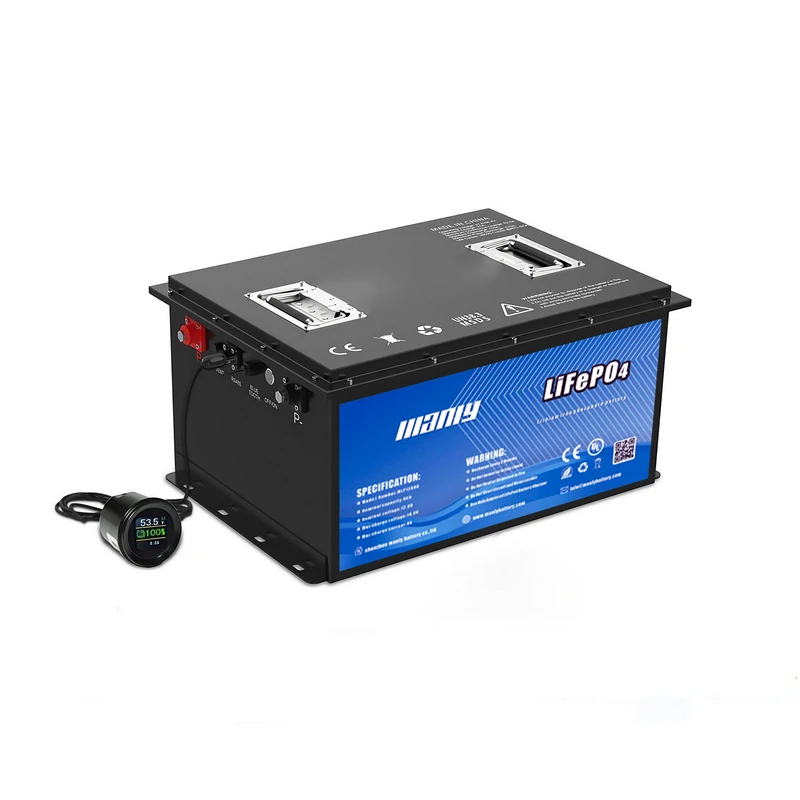
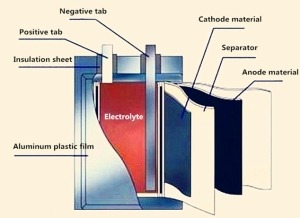
- Baterías: Estos son el corazón de UPS. Almacenan la energía que se utiliza cuando se corta la energía principal.
- Rectificador: Este componente convierte la energía CA (corriente alterna) entrante en CC (corriente continua), cargando la batería.
- Inversor: El trabajo del inversor es cambiar las cosas, convirtiendo la energía CC de la batería en energía CA que sus dispositivos pueden usar.
- Interruptor de derivación estática: Piense en esto como un plan de respaldo. Si algo sale mal con el UPS, este interruptor permite que la energía circule por la parte problemática y siga fluyendo hacia sus dispositivos.
Significado y funcionalidad de la batería del UPS
When we talk about a UPS, or an Uninterruptible Power Supply, we're discussing a critical component in keeping electronic devices running smoothly without interruption. A UPS is essentially a safeguard that ensures our computers, medical equipment, and other electronic devices continue to operate during a power outage. Here, let's explore the meaning of baterías del SAIy su papel en estos sistemas.¿Qué es un SAI?
At its core, a UPS is a system that combines batteries (usually maintenance-free lead-acid batteries) with a main host that converts direct current (DC) from the batteries into alternating current (AC), which is the type of current that powers most of our household and office devices. This ability to seamlessly switch from mains electricity to battery power during electrical interruptions is what defines the UPS. Essentially, it serves three main purposes: voltage stabilization, filtration of electrical noise, and providing an uninterrupted power supply.Funcionalidad de las baterías UPS
The functionality of UPS batteries centers around these critical roles:- Estabilización de voltaje: Cuando se conecta a una fuente de alimentación normal, el UPS regula el voltaje para garantizar un suministro de energía constante que proteja los dispositivos contra picos y caídas de energía, que son comunes durante tormentas u otras interrupciones.
- Filtración de energía: Además de regular la energía, los sistemas UPS también filtran el ruido eléctrico y las interferencias que pueden dañar los componentes electrónicos sensibles o alterar su funcionamiento.
- Energía ininterrumpida: La función más reconocida de un UPS es proporcionar energía ininterrumpida. En caso de un corte de energía, el UPS cambia rápidamente a energía de la batería, lo que garantiza que los dispositivos conectados continúen funcionando sin problemas. Esto es crucial para equipos como servidores y maquinaria médica, que necesitan energía constante para funcionar correctamente.
Aplicación de UPS en Norteamérica y Europa
In North America, large data centers typically use three-phase 480V UPS systems, which differ from the standard three-phase 208V used in other commercial settings. This difference allows for handling the higher power requirements of large-scale operations. Similarly, European data centers often use three-phase 400V systems, aligning with local power standards to ensure efficiency and reliability.Medidas de protección
UPS systems are designed to tackle at least nine different electrical issues, including complete power outages, lightning-induced surges, fluctuations in power frequency, and more. By protecting against these problems, a UPS ensures that not only is the operation of devices uninterrupted, but also that the life span and integrity of these devices are maintained.In summary, a UPS battery plays a pivotal role in modern technology, providing critical backup power, stabilizing voltage, and filtering unwanted electrical noise. Understanding the "UPS battery meaning" helps users appreciate the essential security layer that these systems provide to our digital and medical infrastructures.
Historia del suministro de energía ininterrumpida
The history of the Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a fascinating journey that begins in the early 20th century. This technology, which plays a crucial role in today’s digital and healthcare infrastructures, has evolved significantly from its initial conception to the sophisticated systems we rely on today. Let's dive into the development of UPS systems, exploring key milestones and innovations.Primeros comienzosEl concepto de suministro de energía ininterrumpida surgió en los Estados Unidos. En 1903, se introdujo el primer sistema UPS de Emerson en Los Ángeles, lo que marcó el comienzo de una nueva era en la confiabilidad del suministro eléctrico. Sin embargo, el desarrollo significativo se produjo con John J. Hanley, a quien se le atribuye la invención del UPS moderno.John J. Hanley y su invenciónJohn J. Hanley, concerned with the safety of rail passenger trains which operated on electricity, foresaw the need for a system that could prevent disruptions in electrical supply. His concern was that any failure in the electrical systems could potentially allow a train to travel uncontrollably, posing severe risks to passenger safety.In 1934, Hanley obtained a patent for what he called the "Apparatus for Maintaining an Unfailing and Uninterrupted Supply of Electrical Energy." This innovative device was designed to automatically switch to battery power during a power failure, while an external source would normally charge the battery. This system was the precursor to what we now recognize as the UPS.Evolución de la tecnologíaLos primeros sistemas UPS se basaron en diseños de volante giratorio. Estos primeros sistemas podrían proporcionar energía de respaldo durante un período breve (generalmente entre 20 y 90 segundos) suficiente para manejar cortes breves o permitir el apagado seguro del equipo. El volante giraría a altas velocidades, acumulando energía cinética que, cuando fuera necesaria, se convertiría en energía eléctrica para mantener el suministro de energía temporalmente.Sistemas UPS modernosA medida que avanzaba la tecnología, también lo hacían los sistemas UPS. La introducción de baterías de plomo-ácido sin mantenimiento amplió las capacidades de los sistemas UPS, permitiéndoles proporcionar períodos más prolongados de energía de respaldo y haciéndolos adecuados para una gama más amplia de aplicaciones. Los sistemas UPS actuales varían en tamaño y complejidad, desde pequeñas unidades que protegen computadoras individuales hasta instalaciones masivas que garantizan el funcionamiento continuo de centros de datos completos.Usos e importancia actualesUPS systems are now integral to the operation of critical infrastructure across various sectors. They ensure the continuous operation of hospitals, data centers, financial institutions, and more, safeguarding against data loss and equipment damage that can result from sudden power disruptions.The meaning of UPS batteries in today's context goes beyond just providing backup power; they are a key component in the reliability and efficiency of modern power management systems, supporting a range of critical applications.Componentes de un sistema UPS
Understanding the components of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system is essential for anyone relying on these units to protect their electronic devices from sudden power losses. A UPS does more than just provide backup power; it ensures that your devices can continue running smoothly during power interruptions. Here, we'll break down the main components of a UPS system and explain their functions in easy-to-understand terms.¿Qué es una unidad UPS?
A UPS unit is a device designed to provide backup power to your electronics when the main power source fails. It differs from emergency power systems or standby generators in that it provides near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions by using energy stored in its batteries. This allows critical systems and devices to keep running without interruption during a power outage.Componentes clave de un sistema UPS
- Baterías (batería UPS)
- The battery is the heart of the UPS system. It stores electrical energy in chemical form so it can be converted back to electrical energy whenever it's needed. When the main power is on, the battery charges, and when the power goes out, the battery steps in to provide power. Because of its crucial role, the battery is often considered both a vital asset and a common source of failure in UPS systems. Keeping batteries in good condition is key to ensuring reliable UPS performance.
- Rectificador
- El rectificador tiene un doble propósito en un sistema UPS. Su primera función es convertir la corriente alterna (CA) de la fuente de alimentación principal en corriente continua (CC). Esta CC se utiliza luego para cargar la batería del UPS. La segunda función del rectificador es suministrar CC al inversor cuando el UPS está activo, asegurando que la batería esté siempre lista para funcionar cuando sea necesario. Este componente es crucial porque gestiona el flujo de energía desde el suministro principal al sistema UPS y garantiza que la batería esté cargada correctamente.
- Inversor
- Once the power from the main supply is interrupted or fails, the inverter takes over. The inverter's job is to convert the DC power, which has been either stored in the battery or supplied by the rectifier, back into AC power. This AC power is what your devices need to continue operating seamlessly. The inverter ensures that the transition from main power to battery power is smooth and almost instantaneous, which is crucial for maintaining the operation of sensitive electronic equipment.
- Interruptor de derivación estática
- The static bypass switch is a safety feature in a UPS system. It allows power from the main supply to bypass the UPS components and go directly to the load (your devices). This is especially useful if there's a failure within the UPS itself. By bypassing the faulty components, the static bypass switch ensures that power continues to flow to your devices, providing an additional layer of protection and reliability.
Tipos de sistemas UPS
UPS systems can be broadly classified into three main types based on their working principle: Standby, Line-Interactive, and Online.- UPS en espera (UPS fuera de línea)
- Este es el tipo de UPS más simple y generalmente la opción más rentable. Ofrece protección básica al proporcionar energía desde la batería cuando detecta un corte de energía. La transición a la energía de la batería suele tardar unos 10 milisegundos. Los sistemas UPS de reserva se utilizan ampliamente para computadoras domésticas, hardware de oficinas pequeñas y sistemas de puntos de venta (POS). Su diseño simple contribuye a su confiabilidad y asequibilidad.
- UPS de línea interactiva
- El UPS de línea interactiva ofrece funciones más avanzadas en comparación con el UPS de reserva. Incluye un transformador especial que puede ajustar las fluctuaciones de voltaje, lo que ayuda a mantener una salida de energía constante durante caídas y sobretensiones menores sin tener que cambiar a la batería. Este tipo de UPS también suele tener un tiempo de transferencia más rápido que los sistemas en espera, generalmente menos de 4 milisegundos, y proporciona un mejor acondicionamiento general de la energía. Es adecuado para entornos empresariales y dispositivos que requieren un nivel moderado de protección eléctrica.
- UPS en línea (UPS de doble conversión)
- Los sistemas UPS en línea brindan el más alto nivel de protección al convertir continuamente la energía de CA entrante a CC para cargar la batería y luego nuevamente a CA antes de alimentar los dispositivos conectados. No hay tiempo de transferencia en caso de un corte de energía. Este tipo de UPS puede manejar una amplia gama de problemas de energía, como picos de voltaje, fluctuaciones y ruido, entregando energía limpia y estable. Debido a su complejidad y costo, los sistemas UPS en línea se usan típicamente en aplicaciones de energía críticas, como centros de datos, hospitales y otros entornos donde no se pueden tolerar interrupciones de energía.
- UPS de baja frecuencia: Estos sistemas utilizan un rectificador controlado por silicio (SCR) y un transformador de aislamiento que funciona a la frecuencia de la red pública de 50 Hz. Son conocidos por su robustez y se utilizan comúnmente en aplicaciones que requieren alta capacidad de potencia y confiabilidad.
- UPS de alta frecuencia: Los sistemas UPS de alta frecuencia utilizan tecnología de conmutación de alta frecuencia en sus rectificadores e inversores. Estos sistemas son generalmente más compactos y eficientes que los sistemas UPS de baja frecuencia, con frecuencias de conmutación que van desde unos pocos kHz hasta decenas de kHz. Son adecuados para proteger servidores, instalaciones de telecomunicaciones y otros dispositivos electrónicos sensibles de tamaño pequeño y mediano.