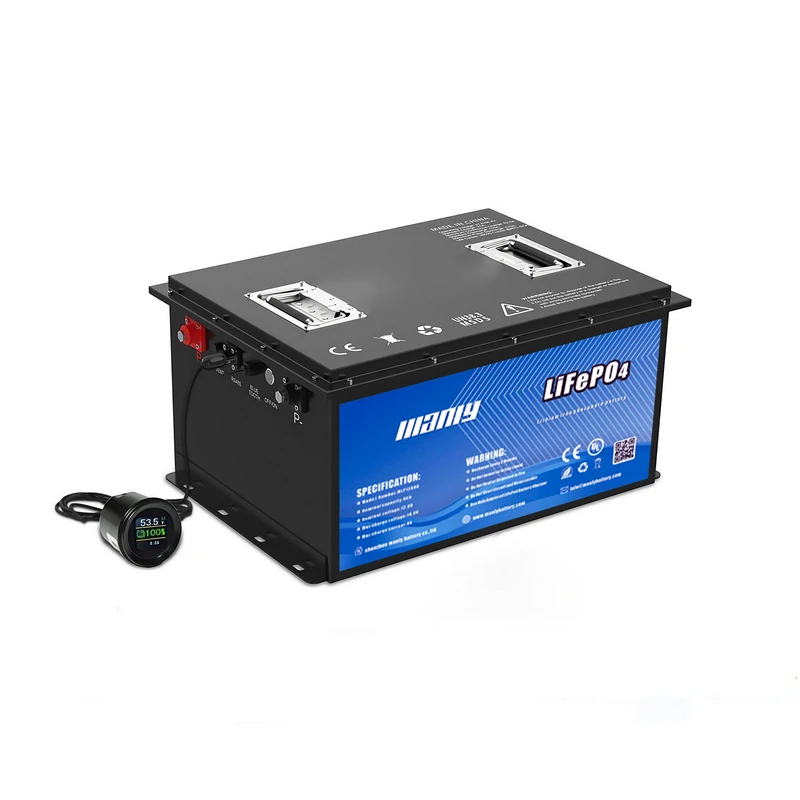
Posso carregar uma bateria de lítio com um carregador normal
Índice
- Posso carregar uma bateria de lítio com um carregador normal
- Escolhendo o carregador de bateria de lítio certo: entendendo as diferenças de carregamento entre baterias de lítio e SLA
- Como as baterias de lítio respondem a um perfil de carregamento SLA
- Um carregador SLA pode danificar uma bateria de lítio?
- Posso carregar uma bateria de lítio com fonte de alimentação?
- Conclusão
- Saiba mais sobre bateria

Escolhendo o carregador de bateria de lítio certo: entendendo as diferenças de carregamento entre baterias de lítio e SLA
Understanding how lithium batteries and SLA batteries absorb charge is essential when choosing the right type of carregador de bateria de lítio. Os perfis de carregamento destas baterias diferem significativamente. As baterias SLA normalmente seguem um processo de três estágios: corrente constante, tensão constante (também chamada de estágio de absorção) e carregamento flutuante. Em contraste, os carregadores de baterias de lítio operam com apenas dois estágios: corrente constante e tensão constante.Processo de carregamento de bateria SLA
For an SLA battery, the first stage is the constant current phase, where the battery receives most of its charge. For example, a 12V 20Ah SLA battery may take around 3-4 hours to reach 80% of its total charge capacity. Once this level is reached, the process shifts to the constant voltage or absorption stage. This stage completes the final 20% of the charge but can take as long as the first stage, making up about 50% of the total charging time. The final stage, float charging, keeps the battery at full charge to prevent self-discharge. While this helps maintain the battery’s lifespan, it also extends the total charging time.Por que a bateria de lítio carrega mais rápido
Charging a lithium battery is much simpler and quicker. With a lithium battery charger, the first stage (constant current) brings the battery up to 99% of its charge. The remaining 1% is topped off in the second stage, constant voltage, which is much shorter than the absorption stage used for SLA batteries. This streamlined process means lithium batteries can be fully charged up to three times faster than similar-capacity SLA batteries.For example, a 12.8V 20Ah lithium battery can reach almost full capacity in about 2.5 hours, compared to over 6.5 hours for an equivalent SLA battery. This rapid charging capability makes lithium battery chargers a popular choice for applications like golf carts, marine systems, and backup power solutions, where minimizing downtime is essential.Perfis de tensão são importantes
One key difference between SLA and lithium batteries is their voltage profiles. A fully charged 12V SLA battery typically reaches around 12.7V, while a lithium battery can reach up to 13.4V when fully charged. This narrow voltage range in lithium batteries means that using a standard SLA charger can lead to either overcharging or undercharging. To prevent these issues, you need a universal lithium battery charger that is specifically designed to meet the precise voltage requirements of lithium batteries.The best way to charge lithium batteries is to use a dedicated li ion battery charger that follows a CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) charging algorithm. This ensures the battery is charged safely and efficiently. Unlike SLA chargers, which may continue to trickle charge, a lithium battery charger stops charging as soon as the battery reaches full capacity, preventing potential damage from overcharging.Como as baterias de lítio respondem a um perfil de carregamento SLA
One common question many people have is whether a lithium battery can be safely charged using an SLA (Sealed Lead Acid) charger. The short answer is: Yes, but there are conditions. To understand why, it’s crucial to look at how lithium batteries absorb charge compared to SLA batteries, especially when using a charger designed for a different type of battery.Como as baterias de lítio respondem aos perfis de carregamento SLA
The main issue when charging a lithium battery using an SLA charger is the difference in the charging curves. Most SLA chargers are set to operate at a constant voltage range between 13.8V to 14.7V. If a lithium battery is charged at the lower end of this voltage range, around 13.8V, it can still reach up to 95% of its total capacity within 90% of the total charging time. This is because the lithium battery’s internal resistance is lower, allowing it to take in more energy more quickly.However, if the charger operates at a higher voltage, around 14.6V—which is the typical voltage used for AGM batteries—the lithium battery can reach up to 99% capacity in just 95% of the charging time. This means that at higher voltages, the charging process is even more efficient, bringing the lithium battery to almost full capacity quickly.Maior tempo de carregamento com um carregador SLA
While a lithium battery can be charged using an SLA charger, the charging time will still be longer than if a dedicated lithium battery charger were used. For example, a 20Ah lithium battery might take around 2.5 hours to charge using a standard lithium battery charger. However, the same battery could take up to 5 hours to charge fully using an SLA charger. This is because the SLA charging profile is not optimized for lithium batteries, leading to less efficient absorption of energy during the constant voltage phase.Despite the longer charging time, a lithium battery will still charge faster on an SLA profile than a typical SLA battery. This is due to the nature of lithium batteries, which can absorb more energy during the bulk charging stage and require less time to reach higher states of charge. So, even with a non-optimized charger, lithium batteries still outperform their SLA counterparts when it comes to overall charging speed.Riscos potenciais de usar um carregador SLA
Although it is technically possible to use an SLA charger for a lithium battery, there are a few important considerations. First, the SLA charger must not have a desulfation mode or a dead battery detection feature. Desulfation mode uses high voltage pulses to restore over-discharged SLA batteries. These high voltage pulses can damage a lithium battery or cause its Battery Management System (BMS) to shut down. Similarly, a dead battery detection mode might misinterpret a lithium battery in protective mode as a dead battery and fail to initiate the charging process.Additionally, the lithium battery charge voltage is more sensitive compared to SLA batteries. Using a charger that outputs voltage outside the acceptable range can harm the battery cells, leading to reduced lifespan or even permanent damage. This is why using a dedicated lithium battery charger or a universal lithium battery charger designed to handle these specific voltage requirements is always the best way to charge lithium batteries.Eficiência de carregamento em diferentes faixas de tensão
The voltage range of the SLA charger will also affect how efficiently a lithium battery charges. At the lower end of the voltage range (13.8V), the lithium battery will charge relatively quickly to 95% SOC, even faster than an SLA battery can reach 80% SOC. When charged at the higher end (14.6V), which is common for AGM batteries, the lithium battery can reach 100% SOC in a shorter time, further highlighting its superior charging capabilities compared to SLA batteries.Overall, while using an SLA charger is not ideal, it can work for charging lithium batteries if no other option is available. However, for the best results and to ensure the longevity of the battery, it’s always recommended to use a dedicated li ion battery charger that can meet the specific charging needs of a lithium battery. This approach minimizes the risks and guarantees optimal performance, making it a safer and more efficient solution in the long run.Um carregador SLA pode danificar uma bateria de lítio?
If you’re using an SLA charger to charge a lithium battery, you might wonder whether it will cause damage. The answer largely depends on the specific features of the SLA charger and how the lithium battery is being used. While it is possible to use a standard SLA charger without immediate harm, several key factors must be considered to prevent long-term damage.Compreendendo os riscos do uso de um carregador SLA
The primary concern when using an SLA charger for a lithium battery is whether the charger has specific modes designed for SLA batteries, such as desulfation or float charging. Desulfation mode, which is intended to restore over-discharged SLA batteries by sending high-voltage pulses, can be highly damaging to a lithium battery. These high pulses may trigger the Battery Management System (BMS) to shut down or, in some cases, physically damage the internal battery cells.Similarly, if the SLA charger includes a float charging mode, it could potentially harm the lithium battery. This mode continuously applies a small current to the battery even after it’s fully charged, which is unnecessary for lithium batteries. Due to their low self-discharge rate, lithium batteries do not need to be kept at 100% state of charge for long periods. Therefore, exposing a lithium battery to float charging over time could reduce its overall lifespan or even lead to overheating.Capacidade limitada com um carregador SLA
One major issue you might encounter when using an SLA charger is that the lithium battery may not reach its full capacity. For example, a 20Ah lithium battery may only charge up to 90-95% of its total capacity using a standard SLA charger. This happens because SLA chargers operate at a slightly different voltage range than a lithium battery charger. This slight voltage difference means the lithium cells are not fully charged, which limits the usable capacity of the battery.If you’re using your lithium battery for a high-demand application, this could lead to reduced performance or shorter run times. However, for low-demand applications, you might not notice the difference. But if maximizing the capacity of your battery is essential, using a dedicated lithium battery charger is highly recommended.Uso diário versus armazenamento de longo prazo
Another critical factor is whether the lithium battery is being used daily or if it will be left connected to the charger for extended periods. If you’re using the battery in a high-cycle application where it’s charged and discharged frequently, an SLA charger without desulfation or float modes may work without causing immediate damage. In these cases, the charger may not keep the battery connected long enough to trigger harmful effects.However, if the battery is going to spend long periods connected to the charger, it’s better to disconnect it once fully charged. Leaving a lithium battery on an SLA charger in storage can lead to unintended float charging, which might negatively impact battery health. Lithium batteries perform best when stored at around 50% state of charge, not at 100%, so it’s crucial to disconnect the battery if it’s not in use.Melhores práticas ao usar um carregador SLA
If you have no choice but to use an SLA charger for your lithium battery, keep the following best practices in mind to minimize potential risks:- Evite usar o modo de dessulfatação: Se o seu carregador SLA incluir um recurso de dessulfatação, não o use. Os pulsos de alta tensão podem danificar uma bateria de lítio ou fazer com que o BMS desligue.
- Desconecte após carregar: Para evitar que a bateria permaneça no modo de carga flutuante, sempre desconecte a bateria de lítio quando ela atingir a capacidade total.
- Monitore os níveis de tensão: Verifique regularmente a tensão da bateria durante o carregamento para garantir que não excede os níveis seguros. Se a voltagem da bateria exceder a faixa recomendada, pare de carregar imediatamente.
- Considere um carregador de lítio dedicado: Para obter melhor desempenho e segurança, mude para um carregador de bateria de lítio. Um carregador de bateria de lítio usará o perfil de carregamento correto e evitará danos potenciais causados por configurações de tensão incompatíveis.
Você pode usar um carregador SLA em aplicações de alto ciclo?
In high-cycle applications, where the battery is frequently charged and discharged, using a standard SLA charger may not cause significant issues if the charger lacks harmful modes like desulfation. This is because the charger won’t be connected long enough to cause float charging or overheating. However, keep in mind that the battery might not reach its full capacity, reducing its effective run time between charges.Ultimately, using a lithium battery charger is always the safest option for maximizing battery performance and lifespan. While it is possible to use an SLA charger temporarily, it’s best to switch to a dedicated lithium battery charger whenever possible.Posso carregar uma bateria de lítio com fonte de alimentação?
The short answer is: Sim, você pode cobrar umbateria de lítiousando uma fonte de alimentação de laboratório, mas requer cuidado e atenção extras às configurações específicas de tensão e corrente. Ao contrário de um dedicadocarregador de bateria de lítio, uma fonte de alimentação não possui recursos de segurança integrados, como regulação automática de corrente durante os estágios de carregamento, portanto, um monitoramento cuidadoso é essencial para evitar sobrecarga ou danos às células da bateria.Como usar uma fonte de alimentação para carregar com segurança
Charging a lithium battery involves following a CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) charging profile. Most commercial lithium battery chargers are designed to automatically adjust the current during the charging process to ensure safe and efficient charging. A lab power supply, however, allows you to manually set the voltage and current limits. This makes it possible to charge a lithium battery, but there are a few critical steps to follow:- Defina o limite de tensão correto: O primeiro passo é garantir que você defina a tensão de saída de acordo com o tipo específico de bateria de lítio. Para baterias de íon-lítio padrão, a tensão deve ser definida para 4,20 V por célula. Para uma bateria LiFePO4 (fosfato de ferro e lítio), o limite de tensão é menor, de 3,65 V por célula. Se você estiver usando um tipo diferente de bateria de lítio, verifique o limite de tensão recomendado pelo fabricante antes de continuar. Exceder a faixa de tensão segura pode resultar em superaquecimento ou danos permanentes às células.
- Defina o limite atual para 1C: A corrente de carga deve ser definida para no máximo 1C, onde C é a capacidade da bateria. Por exemplo, se você estiver carregando uma bateria de 2.000mAh, a corrente não deve exceder 2A. Definir uma corrente muito alta pode causar calor excessivo e danificar potencialmente a estrutura interna da bateria.
- Monitore o processo de carregamento de perto: Ao carregar uma bateria de lítio usando uma fonte de alimentação, é importante monitorar a tensão e a corrente durante todo o processo. À medida que a bateria carrega, ela inicialmente consumirá corrente máxima. Quando a tensão atingir o ponto de ajuste (por exemplo, 4,20 V por célula para um íon de lítio padrão), a corrente começará a diminuir. Este é o estágio de tensão constante, onde a corrente diminui gradualmente à medida que a bateria atinge a capacidade total.
- Pare de carregar quando a corrente cair para 3% do valor inicial: Ao contrário de um carregador de bateria de lítio comercial, uma fonte de alimentação não para de carregar automaticamente quando a bateria está cheia. Para evitar sobrecarga, pare de carregar quando a corrente cair para cerca de 3% da corrente de carga inicial. Por exemplo, se você definir a corrente inicial para 2A, desconecte a bateria quando a corrente cair abaixo de 0,06A.
Usando uma fonte de alimentação versus um carregador de bateria de lítio dedicado
While a power supply can be used to charge a lithium battery, it lacks many of the safety features found in a lithium battery charger. Commercial chargers are designed to handle the unique characteristics of lithium batteries, such as maintaining the precise lithium battery charge voltage and automatically switching off once the battery is fully charged. Using a power supply requires manual oversight, making it more prone to human error.Additionally, a commercial lithium battery charger will step down the current during the constant voltage phase, preventing unnecessary stress on the battery. A lab power supply, on the other hand, will continue supplying the set current, which can lead to overcharging if not monitored carefully. This is why it’s always safer to use a dedicated li ion battery charger whenever possible.Medindo a carga da bateria com um multímetro
To monitor the charge status of your lithium battery, you can use a multimeter to check the voltage. For example, if you’re charging a single Li-ion cell, the voltage should gradually rise from around 3.0V (empty) to 4.20V (full). If you’re charging a pack with multiple cells in series, multiply the per-cell voltage by the number of cells in the pack. It’s also possible to use the power supply’s display to track the charging current and voltage.When the charging current falls to nearly zero (e.g., below 0.01A), the battery is considered fully charged. At this point, disconnect the battery immediately to prevent overcharging.Precauções ao usar uma fonte de alimentação
While it’s possible to charge a bateria de lítiocom uma fonte de alimentação, certas precauções devem ser tomadas para garantir a segurança:- Garanta o equilíbrio adequado: Se você estiver carregando uma bateria com várias células em série, certifique-se de que a bateria tenha um BMS (Battery Management System) com recursos de balanceamento. Isso ajudará a manter cada célula na mesma voltagem e evitará sobrecarga de células individuais.
- Evite sobrecarregar: Nunca deixe uma bateria de lítio conectada a uma fonte de alimentação depois de atingir a carga total. A sobrecarga pode causar superaquecimento, inchaço da bateria ou até mesmo se tornar um risco à segurança.
- Monitorar temperatura: Fique de olho na temperatura da bateria durante o carregamento. Se a bateria ficar muito quente, interrompa imediatamente o processo de carregamento.