Batería de estado sólido versus iones de litio: la guía definitiva
Tabla de contenido
- Batería de estado sólido versus iones de litio: la guía definitiva
- Comprensión de las baterías de iones de litio
- Baterías de estado sólido: ¿el futuro del almacenamiento de energía?
- Las 4 ventajas clave de las baterías de estado sólido sobre las de iones de litio
- What's the Difference Between Solid State Batteries and Lithium-Ion Batteries?
- Cuatro grandes diferencias entre las baterías de litio y de estado sólido:
- The Ultimate Guide: Marine Battery vs Car Battery
- The concept and classification of power tools
- Optimizing Portable X-Ray Machines with Superior Battery Technology
- 12V 150Ah Lithium Battery For Bank Emergency Systems
Comprensión de las baterías de iones de litio
What's a Lithium-Ion Battery?
Abatería de iones de litio is a kind of rechargeable battery. It works by moving lithium ions between two ends called the positive and negative poles. When you charge it, the lithium ions move from the positive pole, go through a middle part, and go to the negative pole. When you use the battery, the ions move back the other way.The first successful lithium-ion battery was made by a Japanese company called Sony in 1990. Instead of using pure lithium, they put lithium ions into carbon for the negative pole. The positive pole often has materials like LixCoO2 or LixNiO2 or LixMnO4. The middle part uses something called LiPF6 mixed with other stuff.
Baterías de estado sólido: ¿el futuro del almacenamiento de energía?
What's a Solid State Battery?
A solid state battery is a new kind of battery. It's not like the common lithium-ion batteries we use today. Instead of liquids, it uses solid parts inside.Scientists think lithium-ion batteries have reached their best. So, they now see solid state batteries as the next big thing. These batteries use a glassy mix of lithium and sodium. This replaces the liquid used in lithium batteries, making them hold more power.In a field called solid-state ionics, these batteries use all solid parts. They might have less power but can store a lot of energy. Because they're light and powerful, they're perfect for electric cars.¿Cómo funciona una batería de estado sólido?
Imagine an old-timey rocking chair. Regular lithium batteries are like this chair. The two ends of the chair are the battery's two poles. The middle part is a liquid. Now, picture lithium ions as runners. They run back and forth between the two ends. As they move, the battery charges and discharges.Solid state batteries are similar. But instead of a liquid middle, they have a solid one. This lets more charged ions gather at one end, moving more electricity. So, solid state batteries can be smaller but hold the same power. Plus, with no liquid inside, they're easier to seal. This makes them great for cars. There's no need for extra cooling or controls, saving money and reducing weight.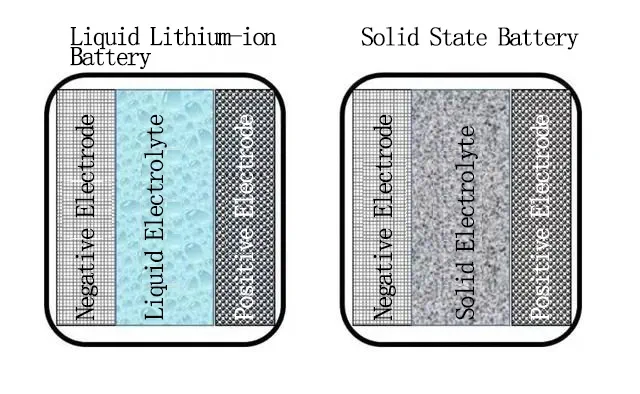
Las 4 ventajas clave de las baterías de estado sólido sobre las de iones de litio
What's the Difference Between Solid State Batteries and Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Solid state batteries and lithium-ion batteries have some big differences. The main one is what's inside. Lithium-ion batteries have a liquid inside, which makes them heavy. And because they don’t hold a lot of power, we need to use many of them together, which makes them even heavier. This makes electric cars expensive because the battery is a big part of the cost.There are other problems with the liquid inside lithium-ion batteries. It can catch fire if the battery gets too hot. If there's a car crash, the battery could start a big fire. The liquid can also freeze in cold weather, making the battery not work as well. Plus, this liquid can wear out parts of the battery over time, and the battery can get these things called dendrites. These problems make the battery not last as long or work as well.Now, solid state batteries don't have this heavy liquid. Instead, they have solid stuff like glass or ceramics inside. They work kind of like lithium-ion batteries but are smaller and more compact. If we replace the batteries in electric cars with solid state batteries of the same size, they could hold over twice as much power.Solid state batteries are also lighter and don't need all the extra stuff that lithium-ion batteries need to stay cool or warm. This means we can fit more batteries in an electric car, giving the car a longer drive range.Cuatro grandes diferencias entre las baterías de litio y de estado sólido:
- Cuánta energía pueden almacenar:Las baterías de estado sólido pueden almacenar más energía para su tamaño y peso que las baterías de iones de litio. Actualmente, las baterías de iones de litio almacenan entre 250 y 300 unidades de energía (Wh/kg). Las baterías de estado sólido pueden almacenar más de 500 unidades.
- Costo: Solid state batteries are more expensive right now. This is because they are new and it's not as easy to make them in big amounts. Lithium-ion batteries have been around longer and are cheaper to make.
- Hasta dónde puedes llegar con una sola carga:Dado que las baterías de estado sólido pueden almacenar más energía, los automóviles que las utilizan pueden llegar más lejos con una sola carga. Esto es especialmente bueno para viajes largos. Pero tardan más en cargarse, lo que puede no gustar a algunas personas.
- Seguridad: Solid state batteries are safer. The liquid in lithium-ion batteries can catch fire or explode if it gets too hot. But, solid state batteries don't have this risk because they don't have this liquid.
| Criterios | Batería de iones de litio | Batería de estado sólido |
|---|---|---|
| ventajas: | ||
| Densidad de energia | Moderado (250-300 Wh/kg) | Alto (>500 Wh/kg) |
| Costo de producción | Menor (Debido a escala y experiencia) | Superior (tecnología más nueva) |
| Madurez | Bien establecido y ampliamente utilizado. | Tecnología emergente |
| Tiempo de carga | Generalmente más rápido | puede ser mas lento |
| Peso | Más pesado debido al electrolito líquido. | Encendedor |
| Seguridad | Puede sobrecalentarse o incendiarse bajo ciertas condiciones. | Más seguro gracias al electrolito sólido (sin fugas ni incendio) |
| Ciclo vital | Puede degradarse más rápido debido al electrolito líquido. | Vida útil potencialmente más larga debido a la estructura sólida |
| Rendimiento en climas fríos | El rendimiento cae significativamente en condiciones de frío | Generalmente mejor rendimiento en condiciones más frías |
| Desventajas: | ||
| Densidad de energia | Más bajo en comparación con el estado sólido | N / A |
| Costo de producción | N / A | Alto debido a la nueva tecnología |
| Madurez | N / A | Aún en desarrollo para el mercado masivo. |
| Tiempo de carga | N / A | Puede ser más lento en comparación con Li-ion |
| Peso | mas pesado | N / A |
| Seguridad | Riesgo de incendio o explosión (Batería varonilPosee tecnología de protección de batería para evitar que las baterías de litio exploten o se incendien durante impactos severos.) | N / A |