Discover the Best: LiFePO4 vs Lithium-Ion Guide
Table of Contents
- Discover the Best: LiFePO4 vs Lithium-Ion Guide
- The Physical Differences Between LiFePO4 VS Lithium-ion Batteries
- What Do These Chemical Differences Do in Terms of Results?
- Applications of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Cold Weather and Battery Performance
- LiFePO4 Batteries: A Safe Battery Choice
- Get Your LiFePO4 Battery from MANLY Battery

The Physical Differences Between LiFePO4 VS Lithium-ion Batteries
First, while the outer housings of both batteries are practically identical in form and function, the internals of both batteries are fairly different.Batteries rely on chemicals to build and store energy, and that’s where these two batteries start to differ, as well as the main difference that impacts their performance.In many ways, it’s similar to having a diesel version of a truck and a non-diesel version of the same truck. They look similar, perform similarly, and have similar systems, but the fuel each one is designed to use produces dramatically different results.Here’s a breakdown of the chemical composition in each one before we move on to the effects these differences produce.Lithium-Ion:
Lithium-ion batteries are a lot more complicated than LiFePO4 batteries in a chemical sense. They’re powered by lithium iron phosphate, cobalt, lithium salt, and lithium manganese oxide in varying amounts and ratios depending on the battery and how it’s manufactured.LiFePO4:
LiFePO4 batteries are lithium batteries that drop all the excess chemicals. They utilize lithium iron phosphate with a carbon anode, and they’re “fed” by a lithium salt electrolyte.There is no manganese oxide or cobalt in LiFePO4 batteries.What Do These Chemical Differences Do in Terms of Results?
While the chemical differences sound minor on paper, they actually produce some dramatically different effects that are crucial in several areas.We’re going to go through each main factor and compare the performance of LiFePO4 vs lithium-ion batteries.1: Energy Density
First, we’re starting off with a category where LiFePO4 actually falls behind considerably. While LiFePO4 has plenty of good uses, lithium-ion is not obsolete.Energy density is essentially how much power a battery can store at once. The more energy-dense the battery is, the more energy the battery holds, and the longer it's going to last without a charge.A standard lithium-ion battery has an energy density of about 120Wh per pound. Whereas, a LiFePO4 battery peaks at 55Wh per pound.That’s only about half the energy density of lithium-ion when you compare their peak statistics.Before you decide there’s too much of a difference to warrant getting a LiFePO4, there’s a caveat to consider.The effects of energy density become a lot less noticeable as the size of a power system scales up. So, if you’re trying to store power for a small device, LiFePO4’s shortcomings are noticeable and impactful on the performance of the device. However, if you’re storing power for an entire home with solar panels, then that issue becomes pretty much unnoticeable.So, this factor is really only relevant depending on what the battery is used for.
2: Safety
Safety is absolutely crucial. When batteries catch on fire or explode, they don’t go out like other sources of fire. They burn extremely hot, and they more or less keep burning until every last bit of fuel is out. They can even reignite after being put out.Obviously, in a residential home powering an in-home workshop, solar panel relay, or something else, a battery failing and causing a fire can be absolutely devastating.This is one area where LiFePO4 batteries are much more reliable than lithium-ion batteries.Since LiFePO4’s chemical composition is more simplistic and lacks several volatile materials found in other lithium battery types, LiFePO4 batteries are a lot more stable.This doesn’t mean that standard lithium-ion batteries are unsafe, but they are more prone to overheating and causing devastating fires in certain use cases.This is one reason LiFePO4 is becoming far more popular in residential solar energy applications. With a series of many batteries hooked up to a household at once, the added safety and reliability are well worth the lack of energy density. A lithium fire in a residential home triggered by multiple large batteries can be worse than in a normal house fire.With LiFePO4, fire hazards are reduced to almost non-existent levels.3: Weight
For stationary usage, this isn’t too much of an issue in most situations. However, there is a considerable weight difference.While lithium-ion is more energy-dense than LiFePO4, it’s also a lot lighter. This is why lithium-ion batteries are so popular in power tools, phones, tablets, and other devices that are constantly being carried around. A LiFePO4 is considerably heavier with less energy density.So, lithium-ion batteries win in this category for many everyday uses, but considering the other areas they win in such as safety, it’s not a major issue. Especially for applications such as off-grid living where the batteries will likely remain unmoved unless they need to be replaced.This is still a factor you should consider if added weight is going to make it difficult to use them in your application; such as using them for an EV bike or other item that needs to minimize weight as much as possible.4: Voltage
LiFePO4 batteries don’t have as high of voltage capabilities as standard lithium-ion batteries.Voltage is measured on a per-cell basis. Whereas a lithium-ion battery can get 3.7 volts per cell, LiFePO4 can only reach 3.2.That doesn’t seem like a major difference, but it does mean that you have to have larger batteries with more cells to achieve the same overall voltage in a LiFePO4 that you get in a standard lithium-ion battery.In fact, this is one reason that LiFePO4 batteries are heavier.This can affect some devices, and it’s worth considering the application you’re using the battery for and its unique voltage needs.However, it’s usually not a major issue as long as you get the right battery size for your usage.5: Self-Discharge
If you’re storing energy for an application that isn’t used every day, then this is a crucial factor to consider. Self-discharge rate is the speed at which a battery depletes on its own when it’s not in use. If you’ve ever had a flashlight with a lithium-ion battery, charged it to full, and then not needed it for months, then you know what it’s like to go to use it, and it’s dead. That’s because of self-discharge.LiFePO4 has the advantage in this category. A LiFePO4 battery will only lose about 3% of its battery over the course of a month. So, if it’s at 100%, and you don’t use it again at all, it’ll take more than 2 years to fully deplete itself.This makes LiFePO4 perfect for emergency power sources because you don’t need to constantly top it off to make sure it’s still charged for when you need it. Simply topping it off every few months is more than enough to keep the battery reliable for your time of need.6: Lifespan
This is one of the advantages of LiFePO4 that is great for every possible usage but makes it the best option for off-grid options. LiFePO4 lasts about 6 times longer on average.A standard lithium-ion battery starts to lose its performance after about 500 charge cycles. The battery doesn’t become useless, but you’ll notice it dies faster, charges slower, and eventually, just doesn’t take a charge at all.LiFePO4 can be charged around 5,000 times before it has any noticeable performance drops.This means that you can more or less “set it and forget it”, which is crucial when you’re in an off-grid situation long-term, and of course, it means you have to buy fewer replacements. The latter plays into our next major advantage.7: Price
Finally, we can break down the price difference.At first, standard lithium-ion varieties seem like the better deal. They’re more energy-dense, weigh less, and yes, they cost less.However, LiFePO4 only costs a little more, and beyond the other benefits we’ve talked about, you have to consider its expected lifespan.LiFePO4 lasts about 6 times longer than standard lithium-ion. So, if you have to replace a lithium-ion battery once a year in the application you’re using it for, you might get 6 years of performance out of a LiFePO4 battery.That makes LiFePO4 considerably cheaper in the long term despite the higher initial cost.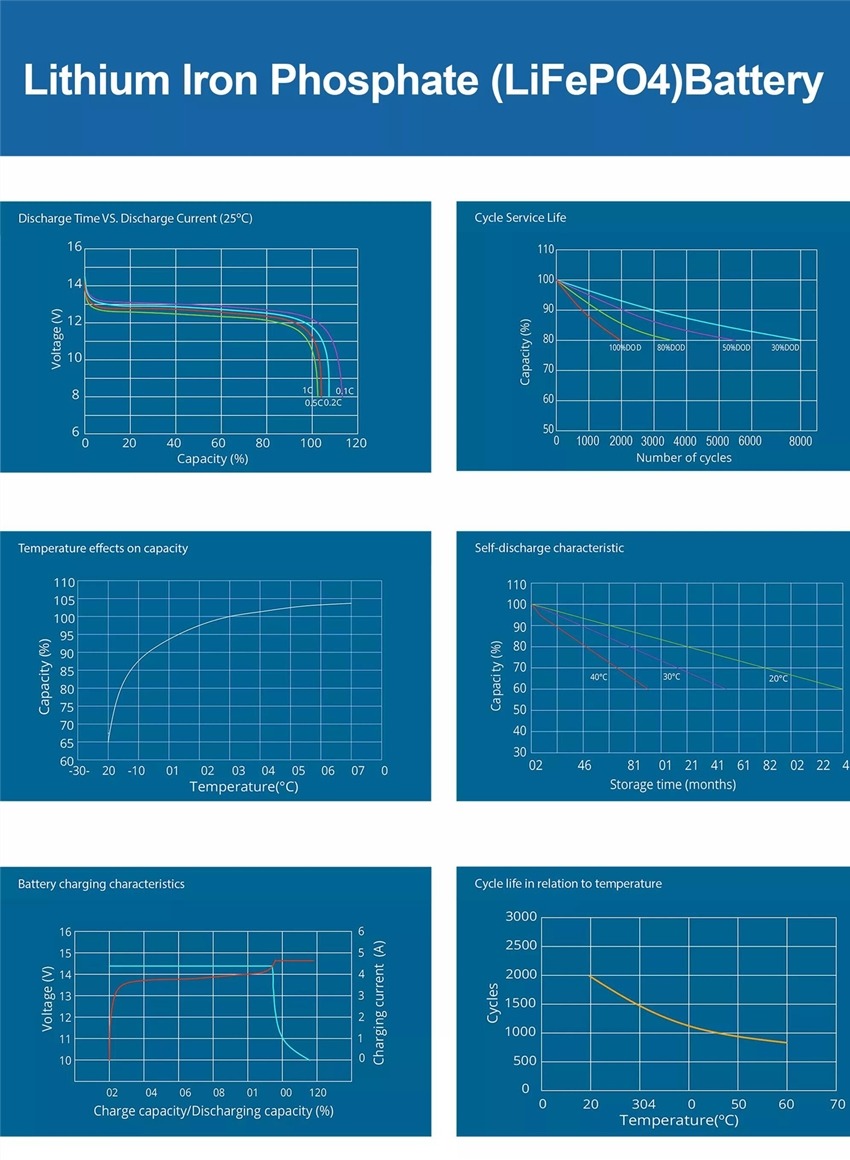
Applications of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-based batteries have revolutionized modern electronics, enabling the design and creation of compact, powerful devices. Let's explore the distinct applications of both Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Lithium-Ion batteries.Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Applications:- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Due to their enhanced safety and longer lifespan, LiFePO4 batteries are becoming increasingly popular in EVs. They can handle high temperatures and are less prone to overheating, making them ideal for vehicular applications.
- Medical Devices: The reliability and safety profile of LiFePO4 batteries makes them a favored choice for critical medical equipment where dependability is paramount.
- Military Equipment: Devices used in defense and military applications are often exposed to extreme conditions. The sturdy nature of LiFePO4 batteries ensures their optimal performance under challenging environments.
- Stationary Power Systems: LiFePO4 batteries, being slightly bulkier and heavier, find their place in stationary power systems, including off-grid solar systems and backup power solutions.
- Cost Efficiency: Manufacturers, looking at the broader picture of production and disposal costs, often opt for LiFePO4. Its chemistry, which is inherently safer, results in lower recycling expenses.
- Portable Electronics: Lithium-Ion batteries, with their high energy density, are the go-to choice for devices where compactness is vital. Think of your smartphones, laptops, tablets, and even electronic cigarettes.
- High-Energy Devices: Devices that demand top-notch performance right off the bat, like high-end cameras or drones, often rely on the energy-rich chemistry of lithium-ion batteries.
- Size Constraints: In scenarios where device dimensions are limited, the compactness of lithium-ion batteries gives them an edge. Their ability to store more power in a smaller footprint is unparalleled.

Cold Weather and Battery Performance
Cold weather can be challenging, not just for us humans but also for our electronic devices. Let's delve into how sub-zero temperatures can impact battery performance, especially lithium-based batteries.Effects of Cold Weather on Batteries:- Decreased Functionality: Most batteries, when exposed to freezing temperatures, experience a drop in their operational efficiency. In some instances, they might even stop working entirely.
- Lithium Batteries and Cold: Lithium batteries, in particular, are quite sensitive to chilly conditions. They can freeze and cease to function below a certain temperature threshold.
LiFePO4 Batteries: A Safe Battery Choice
When it comes to batteries, safety is a priority. Among the various types of batteries available today, the question often arises - "Are LiFePO4 batteries safe?" Let's explore the safety features of these batteries.Safety Characteristics of LiFePO4 Batteries:- Stability: LiFePO4 batteries might not have the same energy density as Li-ion batteries, but they make up for it in stability. This stability makes them a top choice for applications where safety is paramount, such as in RVs.
- Eco-friendly: A major advantage of lithium iron phosphate (the primary component in LiFePO4 batteries) is that it's non-toxic. This means that disposing of these batteries is more environmentally friendly compared to lead-acid or Li-ion batteries.
- Integrated BMS: Unlike traditional lead-acid or AGM batteries, most LiFePO4 batteries come equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS). This system ensures that the battery charges and operates efficiently and safely, providing an added layer of protection.
- Resilience to Thermal Runaway: One of the standout features of LiFePO4 batteries is their resistance to thermal runaway. In simpler terms, they're designed to prevent overheating, making them safer not just for users but also for the surrounding environment.
- Superior to Lead-Acid or AGM: While lead-acid or AGM batteries have their uses, they don't match up to the safety standards set by LiFePO4 batteries. The lack of a BMS in lead-acid batteries means they're more prone to damage and overheating during charging and discharging phases.



















