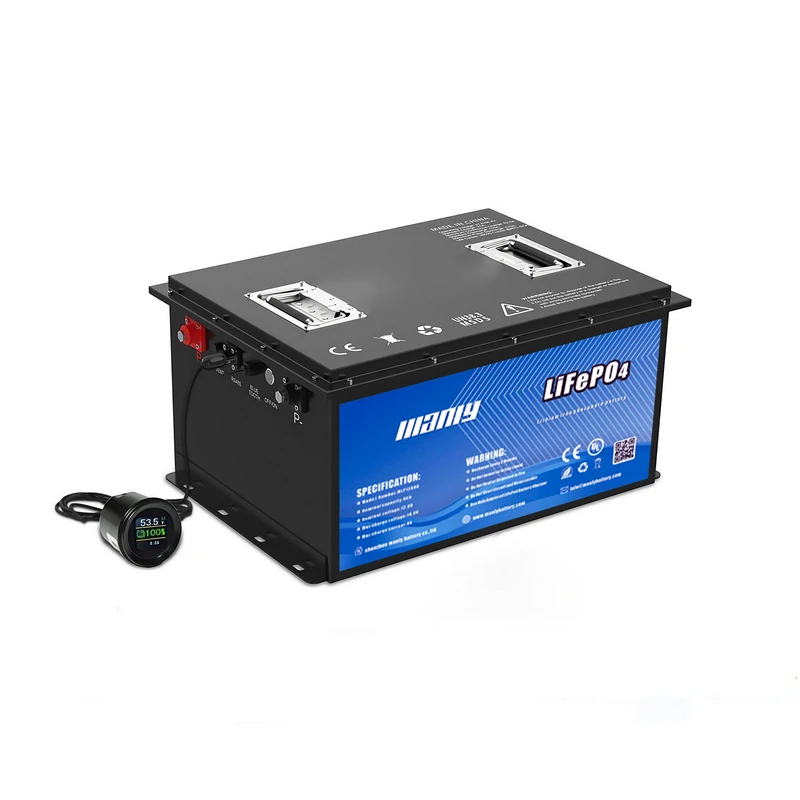
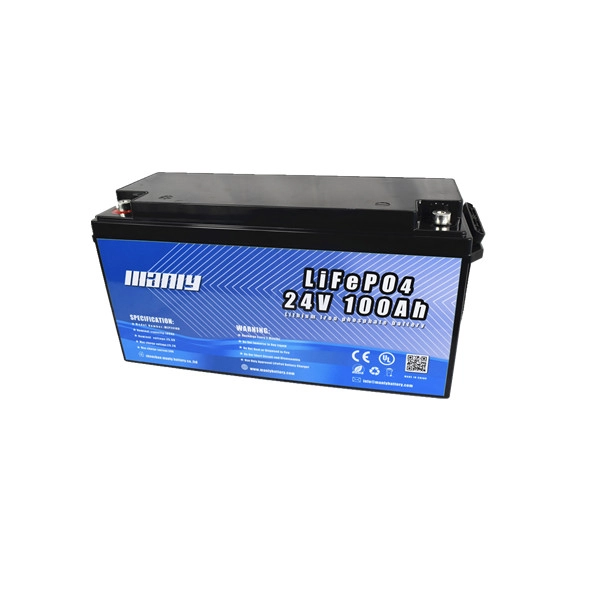
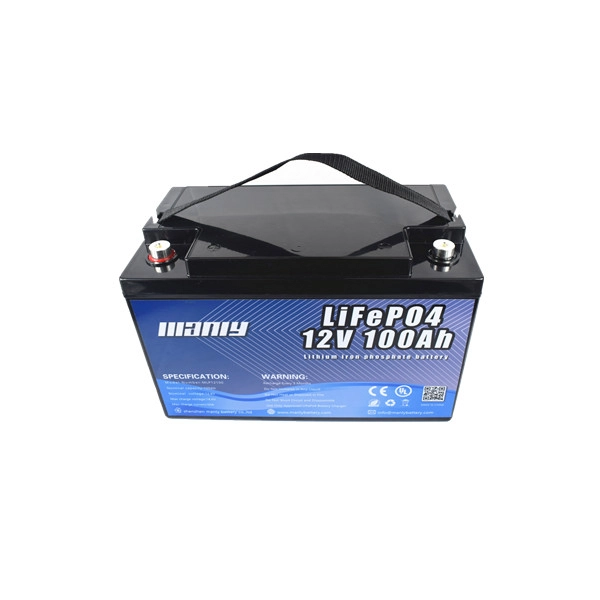
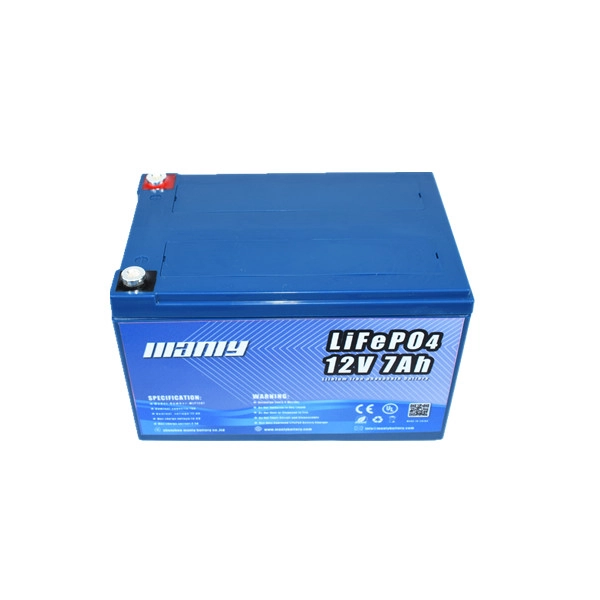
Commonly known as the "four major pieces" that make up an electric vehicle refer to the electric vehicle battery, motor, controller and charger. The following is an introduction to the functions, structure and functions of the "Four Major Items":One: Electric vehicle battery: It is the power source of electric vehicle, the energy carrier, used to drive the motor, the voltage of the electric vehicle battery determines the working voltage of the vehicle, and the battery capacity of the electric vehicle is directly proportional to the continuous journey of the vehicle.
The structure of lead-acid electric vehicle batteries commonly used in electric vehicles is mainly composed of electric vehicle battery shells, positive plates, negative plates, separators, electrolytes, terminals, sealants, safety valves and other components.The types of electric vehicle batteries can be divided into: lithium-ion electric vehicle batteries, nickel-metal hydride electric vehicle batteries, gel electric vehicle batteries and maintenance-free lead-acid electric vehicle batteries. Among them, gel electric vehicle batteries and lead-acid electric vehicle batteries are commonly used.
According to the voltage, it can be divided into 6V, 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, 60V, 64V, etc. The most commonly used electric vehicle is 48V.According to the capacity specifications, it can be divided into: 10AH, 12AH, 17AH, 20AH, 22AH, etc. 12AH and 20AH storage battery batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles.Two: Motor: Converts the chemical energy of the electric vehicle battery into mechanical energy, and converts the rotational energy into mechanical traction, so that the wheels rotate. The working voltage of the motor is inversely proportional to the working current, and the power of the motor is proportional to the climbing ability.
According to the way of energization, it can be divided into brush motor and brushless motor:A: Brushed motors are composed of iron core windings, magnetic steel sheets, carbon brushes, carbon brush holders, commutators, etc. The regular operation effect is achieved by the exchange of contact between the carbon brushes and the commutator.B: The brushless motor is composed of iron core windings, magnetic steel sheets, Hall elements, etc. It relies on Hall (dielectric degree angle) commutation to achieve regular operation.
According to the structure, the motors can be divided into: brushless and toothless, brushless and toothless, brushless and toothed, and brushed and toothed, etc. The most commonly used is brushless and toothless motors.
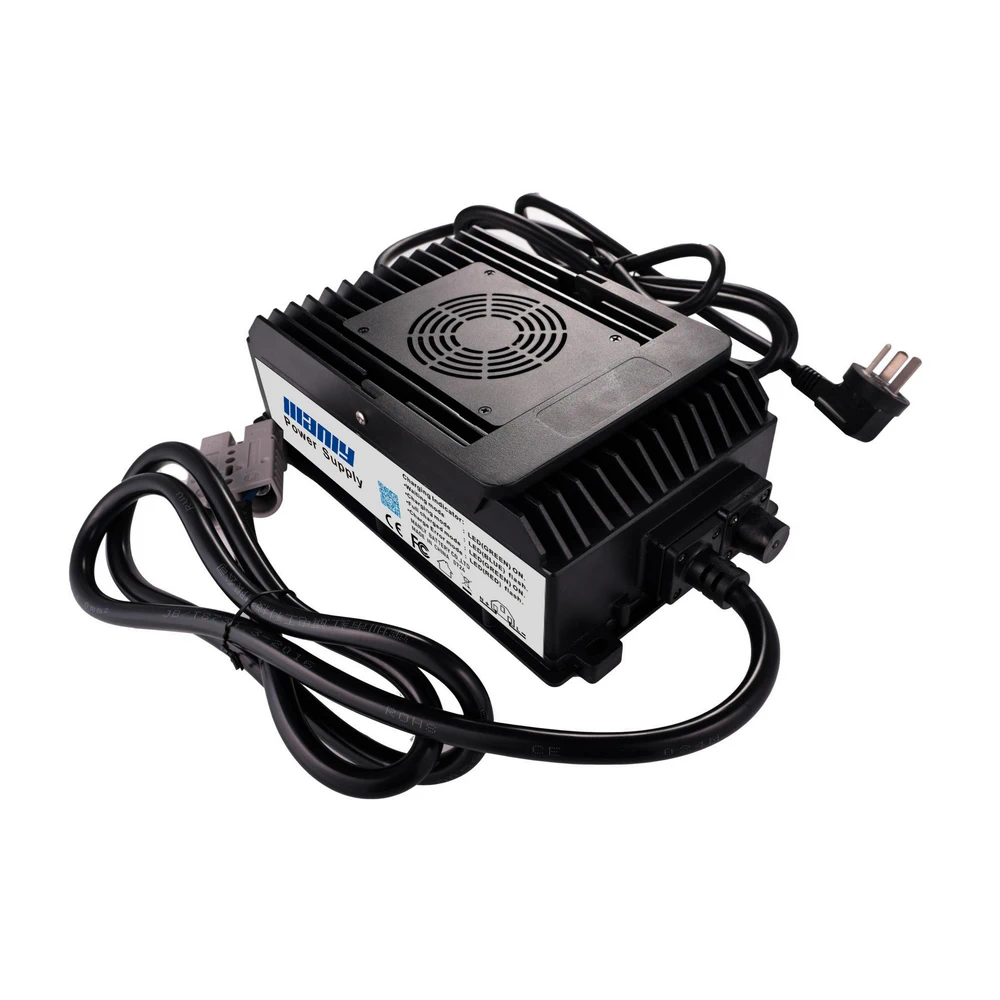
According to the working voltage, it can be divided into: 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, 60V, 64V, etc. The most commonly used is the 48V motor.According to the power, it can be divided into: 180W, 250W, 350W, 500W, 800W, 1000W, etc. The most commonly used are 350W and 500W motors.Three: Controller: Control the output current of the electric vehicle battery, the voltage and then achieve the control of the motor speed and power, that is, the speed of the entire vehicle, to achieve the effect of controlling the entire vehicle. The main functions include stepless speed regulation, brake power failure, current limit protection, undervoltage protection, speed limit, speed display, 1:1 power assist, etc.According to the difference of function and structure, it can be divided into two types: brush controller and brushless controller.According to the working voltage, it can be divided into: 24V, 36V, 48V, 60V, 64V, etc. The most commonly used is the 48V controller.According to the output power, it can be divided into: 180W, 250W, 350W, 500W, 800W, etc. The most commonly used controllers are 350W and 500W.Four: Charger: It is a device that supplements the energy of the electric vehicle battery to charge the electric vehicle battery. It can convert the mains electricity into direct current and control its current and voltage to charge the electric vehicle battery and store it.The charger is mainly composed of rectifier and filter, high voltage switch, voltage exchange and electric control. The working state has three stages: constant current, constant voltage and floating charge.
A: Constant current depends on the type of electric vehicle battery;B: Constant voltage is determined according to the standard of electric vehicle battery. Conventionally, the single-cell voltage is 14.7V—14.8V.C:Floating charge is determined according to the standard of electric vehicle battery, and the conventional single-cell voltage is 13.8V-14V.
Contact Us
For bulk purchases, special surprise pricing will be available. For larger quantities, contact us at [email protected] or fill out the form below.