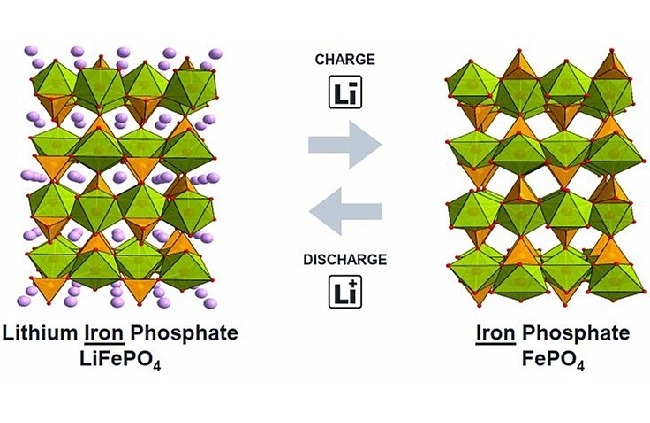
The influence of low temperature on lithium iron phosphate battery
At present, lithium iron phosphate battery is one of the most widely used batteries on the market. This kind of battery has high safety and long cell life. However, the low temperature performance of lithium iron phosphate battery is slightly worse than that of batteries of other technical systems.
Low temperature has an impact on the positive and negative electrodes, electrolyte and binder of lithium iron phosphate. The lithium iron phosphate positive electrode itself has relatively poor electronic conductivity and is prone to polarization in low temperature environments, thereby reducing battery capacity; affected by low temperature, the speed of graphite lithium insertion is reduced, and metal lithium is likely to precipitate on the surface of the negative electrode. If it is left for insufficient time after charging, put it in When used, the metal lithium cannot be fully embedded in the graphite again, and part of the metal lithium continues to exist on the surface of the negative electrode, which is very likely to form lithium dendrites, which affects battery safety; at low temperatures, the viscosity of the electrolyte will increase, and the lithium ion migration resistance will also increase. In addition, in the production process of lithium iron phosphate, the adhesive is also a very critical factor, and low temperature will also have a greater impact on the performance of the adhesive.
Therefore, lithium iron phosphate batteries are not recommended to be used at low temperatures.