Top 5 Battery Choices for Your Electric Scooter in 2023
Table of Contents
- Top 5 Battery Choices for Your Electric Scooter in 2023
- 1. Mastering the Basics: The What and Why of Electric Scooter Batteries
- 2. Demystifying Battery Specs: A Scooterist’s Guide to Battery Terms
- 3. Batteries Unveiled: A Deep Dive into Various Battery Types
- 4. Voltage Sag: The Hidden Drain on Your Scooter’s Power
- 5. Capacity Rating: How Much Juice Does Your Scooter Really Have?
- 6. C Rate: Unraveling the Mystery of Your Scooter’s Battery Discharge Rate
- 7. Tips to Keep Your Electric Scooter Long Battery Life
- 8. Warning Signs: Spotting a Failing Electric Scooter Battery Before It’s Too Late
- 9. Preventing Electric Scooter Battery Fires: Safety Measures You Need to Know
- 10. Conclusion
1. Mastering the Basics: The What and Why of Electric Scooter Batteries
In the world of electric scooters, it’s essential to understand the key role of batteries. They’re not just power sources – they dictate your scooter’s performance, speed, range, and lifespan.
Now, what exactly is an electric scooter battery? Simply put, it’s your scooter’s powerhouse. It stores and discharges electricity to keep your ride moving. From powering the motor to lighting up the headlights, the battery is crucial to every electric component on your scooter. Without it, your e-scooter is just a deck with wheels.
Why is the type of battery so critical? It’s simple – not all batteries are built the same. You’ll find various types like Lead-Acid, Nickel-Metal Hydride, Li-Ion, and LiFePO4 in the market. Each type comes with its pros and cons, affecting your scooter’s performance.
For instance, consider the chemistry behind these batteries. Lead-Acid batteries may be more affordable, but they’re heavier and have a shorter lifespan. On the other hand, lithium batteries, like Li-Ion or LiFePO4, are lightweight and long-lasting, but they cost more upfront.
Next, let’s talk about capacity – a crucial measure of a battery’s energy storage. It’s usually denoted in Ampere-hours (Ah). A higher capacity means a longer ride range for your scooter. So, a 20Ah battery will typically provide a longer range than a 10Ah battery, all other factors being equal.
In summary, your e-scooter’s battery is more than just an energy storage unit. It impacts the performance, range, and longevity of your ride. A basic understanding of its workings can help you optimize your e-scooter experience. We’ll delve deeper into different battery types in the following sections. Stay tuned!

2. Demystifying Battery Specs: A Scooterist’s Guide to Battery Terms
Navigating the world of battery specifications can feel like learning a new language. But don’t fret, in this section, I’ll help demystify some common battery terms for the avid scooterist.
Let’s start with ‘voltage’. You may have seen e-scooter batteries described as 36V, 48V, or 52V. ‘V’ stands for volts, the unit of voltage. Simply put, voltage is the ‘push’ that gets the electricity flowing. It’s like water pressure in a hose. The 36v in an electric scooter battery 36v tells us its voltage is 36 volts. Higher voltage means more power, leading to a faster scooter.
What about 12 volt battery for electric scooter? This is a lower voltage battery. It delivers less power, but it’s lighter and cheaper. It’s often seen in smaller, less expensive scooters.
Now, 48v lithium battery for electric scooter. This one packs a lot of power. Its high voltage is perfect for faster, more powerful scooters. Yet, it’s still relatively light and compact, thanks to its lithium construction.
Next up is ‘capacity’, usually measured in Ampere-hours (Ah). It’s a measure of how much energy a battery can store. For instance, a 10Ah battery can theoretically deliver a current of 10 Amps for an hour. Higher capacity usually equals a longer ride range, all other factors being equal.
You might also come across the term ‘C rate’. It refers to the rate at which a battery is discharged relative to its maximum capacity. A 1C rate means the discharge current will drain the entire battery in one hour.
Let’s talk about ‘Voltage Sag’. It’s the temporary drop in a battery’s voltage under load. You might notice your e-scooter slowing down a bit when climbing hills, even though the battery isn’t low. That’s voltage sag in action!
One more critical term is ‘Battery Management System’ or BMS. It’s like the battery’s personal assistant, ensuring it charges and discharges safely and efficiently. A good BMS can prolong your battery’s life and keep it in top shape.
Finally, you may hear about ‘Swappable Batteries’. These are exactly what they sound like – batteries you can swap out. This feature is becoming increasingly popular in e-scooters. It allows you to extend your range by carrying a spare, fully-charged battery.
So, there you have it. A quick guide to common battery specifications. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll find it easier to understand battery specs and make informed choices when buying or maintaining your e-scooter. But the learning doesn’t stop here. Stay tuned as we dive deeper into specific battery types in the next section!
3. Batteries Unveiled: A Deep Dive into Various Battery Types
3.1 Lead-acid Batteries:
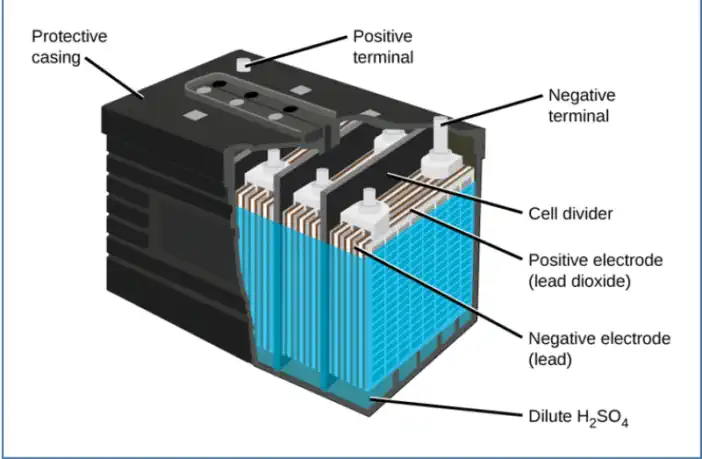
As we delve into our battery exploration, let’s first turn our attention to the age-old contender in the realm of electric scooter power: Lead-acid batteries.
Rooted in an age-old technology, lead-acid batteries are quite similar to the battery you’d find under the hood of your car. They’re known for their reliability, making them a common choice for a wide array of rechargeable battery applications. Need a burst of power to start a car? A lead-acid battery gets the job done. However, they’re not without their shortcomings.
The most glaring downside of lead-acid batteries lies in their energy density, which is markedly poor. Simply put, energy density tells you how much energy a battery can store relative to its weight. In this arena, lead-acid batteries disappoint. They are notably heavy for the amount of energy they contain. In comparison, Li-ion batteries (a category we’ll delve into later) outperform lead-acid batteries by about tenfold in terms of energy density.
So, where do we often find these hefty power storages? They’re commonly used in golf carts, forklifts, and, notably, kids’ e-scooters. Companies like Razor offer inexpensive electric scooters for children powered by lead-acid batteries.
Yet, their appeal lies in their price tag. These batteries are relatively inexpensive, which often makes them an appealing choice, especially for lower-priced electric scooters designed for young riders.
In a nutshell, while lead-acid batteries bring reliability and a friendly price tag to the table, their poor energy density and weighty nature make them less than ideal for more demanding electric scooter applications. Keep reading as we dive into more efficient, lightweight alternatives in the upcoming sections.
3.2 Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries:
Shifting gears, let’s now explore the realm of Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries, the under-the-radar workhorses of the electric scooter world.
As a newer technology compared to lead-acid, Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries (commonly referred to as NiMH) provide a significant upgrade in performance. They’re characterized by better energy density, meaning they pack more power into a lighter package. This trait alone makes them a go-to choice for those desiring a less weighty ride without compromising on power.
But here’s the kicker: NiMH batteries boast a lower self-discharge rate. In other words, they hold their charge longer when not in use. This makes them an appealing choice for scooter enthusiasts who don’t ride daily but want their scooters ready to roll when they are.
On the environmental front, NiMH batteries score some points, too. They contain no toxic heavy metals (like lead or cadmium), making them a more eco-friendly option. This attribute aligns well with the environmentally conscious ethos that drives many electric scooter users.
However, it’s not all sunshine and roses. Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries tend to be more expensive than their lead-acid counterparts. Additionally, they have a shorter overall lifespan and can exhibit a “memory effect” — a phenomenon where batteries lose their maximum energy capacity when repeatedly recharged after being only partially discharged.
In summary, Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries offer a valuable step up from the dated lead-acid technology, providing enhanced energy density and longer charge retention. While they command a higher price and may not last as long, their environmental friendliness and performance perks make them a worthy contender in the world of electric scooter power sources. Stay tuned as we delve into even more advanced battery technologies in the sections to come.
3.3 Li-Ion Batteries:
Next in line, we have the big players in the electric scooter battery game – Li-Ion batteries. Renowned for their high-energy density, Li-Ion batteries pack a punch, delivering considerable power while maintaining a relatively light footprint. This optimal energy-to-weight ratio is a significant factor in their popularity among electric scooter enthusiasts.
The versatility of Li-Ion batteries is another feather in their cap. This technology hosts a variety of chemistries, each having its unique characteristics and strengths. From Lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4) and Lithium manganese nickel (LiNiMnCoO2) to Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), each variant presents a different trade-off between performance and safety.
Now, let’s crunch some numbers. Compared to technologies like Ni-Cd (Nickel-Cadmium) or Ni-MH (Nickel-Metal Hydride), Li-Ion batteries can deliver three times more energy. This high output, coupled with their excellent longevity, ensures that they stay power-ready for a long haul, making them an attractive choice for frequent riders.
Maintenance? With Li-Ion batteries, you can strike that off your list. These batteries are low-maintenance, freeing you from the need for scheduled cycling to retain battery life. Moreover, they’re immune to the memory effect, a notorious issue with some battery types where repeated partial charge-discharge cycles lower the overall capacity.
However, it’s not a complete smooth sailing with Li-Ion batteries. They are prone to overheating and can incur damage at high voltages. Hence, they require built-in safety mechanisms to keep internal pressure and voltage in check, occasionally adding to their weight and marginally limiting performance.
Li-Ion batteries also age over time, losing capacity and starting to falter after several years. Yet, considering their overall performance and longevity, many users see this as a worthwhile trade-off.
To sum it up, Li-Ion batteries, despite a few hiccups, offer a solid, efficient, and reliable power source for electric scooters, keeping you on the move with minimum fuss. As we proceed further, we’ll explore another exciting addition to this league – the game-changing LiFePO4 batteries.
3.4 Lithium Manganese (INR, NMC):
If you’re seeking a safe, high-capacity choice for your electric scooter battery, Li-Ion batteries, particularly those with INR chemistry, are a top choice. These batteries have cemented their place as favorites among electric scooter enthusiasts and for good reason.
The INR, or Lithium Manganese Nickel, battery chemistry is hailed as one of the safest. These batteries don’t just offer high capacity; they also provide high output current. Thanks to the presence of manganese, the internal resistance of these batteries is reduced, allowing for high current output while maintaining cooler temperatures. As a result, this reduces the chances of thermal runaway and fire, contributing to the overall safety of your electric scooter. It’s no wonder that quality electric scooters like the WePed GT 50e and various Dualtron models are equipped with INR batteries.
But safety isn’t the only upside of these batteries. Li-Ion batteries with INR chemistry also shine in terms of energy density and longevity. With a higher energy density, these batteries can store more power, extending the range of your electric scooter ride. In terms of longevity, these batteries have a longer lifecycle compared to cobalt-based batteries, all the while being more cost-efficient.
More so, INR batteries exhibit superior thermal stability than their LCO counterparts, adding another layer to their safety profile. This makes them a common choice not just for electric scooters, but also for power tools and e-bikes.
However, every coin has two sides, and INR batteries are no exception. Despite their plethora of benefits, they do have a minor shortcoming. These batteries deliver a slightly lower voltage than cobalt-based batteries. But for many scooterists, the high capacity, safety, and cost-efficiency of INR batteries more than makeup for this small drawback.
In conclusion, if you’re looking for a high-flying favorite in the realm of electric scooter batteries, Li-Ion batteries, particularly those with INR chemistry, certainly make the cut. Their blend of safety, power, and longevity offers an unmatched riding experience, helping you make the most of your electric scooter adventures.
3.5 LiFePO4 Batteries:
LiFePO4 batteries are turning heads in the e-scooter world. They’re hailed as the future powerhouse. Why? Well, for several reasons.
Firstly, they hold a high energy density. That’s tech talk for ‘they store a lot of power’. The numbers? They’re around 90-120 Wh/kg. That means long rides, less charging.
Second, they have an impressive life cycle. We’re talking 2000 to 5000 charge cycles. Far beyond their competitors. What does that mean? Your e-scooter will run longer and stronger, giving you miles and miles of smooth rides.
Cost is a factor too. Yes, they are pricier. But consider this, their longevity means you’ll replace them less often. Long-term, you’ll save money. And time.
Lastly, let’s talk safety. LiFePO4 batteries have excellent thermal stability. They’re less likely to overheat, reducing the risk of battery fires. That’s a big check for safety.
In summary, LiFePO4 batteries are a great choice for e-scooters. They offer high power, long life, cost efficiency and safety. The future looks bright with LiFePO4 leading the charge.

| Attribute | Lead-acid Battery | NiMH Battery | Li-Ion Battery | INR (NMC) Battery | LiFePO4 Battery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 33-42 | 60-120 | 150-200 | 150-220 | 90-120 |
| Life Cycle | 500-800 | 500-1000 | 1000-2000 | 1000-2000 | 2000-5000 |
| Self-discharge rate (%/month) | 5 | 20-30 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| C Rate | 1C | 1C-2C | 1C-2C | 2C-3C | 1C-2C |
| Nominal Voltage (V) | 12 | 1.2 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.2 |
| Usable Capacity (Ah) | 7.5 – 20 | 2 – 9 | 2 – 3 | 2 – 3 | 10 – 100 |
| Cost | $ | $$ | $$$ | $$$ | $$$ |
| Overall Evaluation (stars) | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
4. Voltage Sag: The Hidden Drain on Your Scooter’s Power
There’s a sneaky culprit in your scooter’s battery system that might just be draining your power: voltage sag. But what exactly is it?
When you kickstart your e-scooter and put a demand on the battery, the voltage instantly drops. It’s like a mini power outage, and if you’re keeping an eye on your battery voltage, it might seem like you’ve just lost a significant chunk of your power. But don’t panic just yet. Once the load eases off, the battery voltage bounces back to its real level.
A few culprits can be behind this phenomenon. It could be the surge of energy needed to start the motor, a bit of electrical resistance, temperature fluctuations, or even a dodgy component. Draining the battery to its last drop can also trigger voltage sag, as the lithium in the battery struggles to keep up with the discharge rate. Hence, the voltage drop accelerates the longer you ride.
But rest assured, your battery just needs a little downtime. Giving your scooter battery some rest time allows it to recover to its true voltage level. So next time you notice a sudden dip in power, remember, it’s probably just voltage sag doing its thing.

5. Capacity Rating: How Much Juice Does Your Scooter Really Have?
Have you ever wondered how much ‘juice’ your e-scooter can really hold? That’s where the capacity rating comes into play.
Rated in units called watt-hours (Wh), capacity rating is essentially a measure of the energy your e-scooter’s battery can store. Think of it like this: a 1 Wh rated battery can sustain one watt of power for a full hour.
And yes, size does matter. The higher the battery’s watt-hour rating, the greater its energy capacity. This means it can power your scooter for a longer range, assuming the motor size is constant. Your average scooter, for instance, usually has a capacity of around 250 Wh, translating into about a 10-mile journey at an average speed of 15 miles per hour.
But what about the big guns? Well, some of the high-performance e-scooters can boast thousands of watt-hours in capacity, empowering them to cover distances of up to 60 miles. So the next time you check your scooter’s battery, remember – it’s all about the watt-hours!
6. C Rate: Unraveling the Mystery of Your Scooter’s Battery Discharge Rate
Welcome to another fascinating feature of your e-scooter’s battery – the C-rate. This mysterious little number is all about speed; specifically, how quickly your battery charges or discharges.
Here’s how it works. A battery with a C-rate of 1C can be fully juiced up in one hour. Easy enough, right? Now, a C-rate of 2C means your battery will be fully charged in just half an hour. On the flip side, a 0.5C C-rate would require two hours to fully charge.
But it’s not all about charging. The C-rate can also tell us about the battery’s discharge speed. Say you have a fully charged battery with a capacity of 10Ah. At a C-rating of 1C, it can provide 10 Amps for one hour. If you’re working with a 0.5C C-rate, it’ll give you 5 Amps over two hours. And for a 2C rate? You’d get 20 Amps for half an hour.
In essence, your battery’s C-rate provides valuable insights into the speed at which it can deliver or replenish its stored energy. Quite a useful bit of knowledge to have under your belt, isn’t it?
7. Tips to Keep Your Electric Scooter Long Battery Life
Riding your electric scooter is fun, no doubt about it. But keeping your electric scooter battery time longer? That’s where the real satisfaction comes in. When it comes to Li-ion batteries, like those powering your e-scooter, you’re looking at about 300 to 500 charge/discharge cycles before seeing a noticeable drop in capacity. Put in perspective, that’s a whopping 3,000 to 10,000 miles on an average scooter!
Now, don’t panic when you hear “drop in capacity”. It doesn’t mean your battery’s on its last legs. Rather, you might notice a 10 to 20% decrease in capacity that gradually worsens over time. Thanks to modern battery management systems, you won’t need to stress too much over prolonging electric scooter battery time. But if you’re all about efficiency, there are a few things you can do to stretch those cycles even further.
Avoid storing your scooter with the charger plugged in or when it’s fully charged for long periods. Similarly, don’t let your scooter’s battery get too low. Most manufacturers recommend storing your scooter with about 50% charge, and topping it up to this level now and then for extended storage. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, are no friends to your battery. Stick within 32 to 113 degrees Fahrenheit for optimal performance. And finally, consider charging at a lower C-rate, which means charging your battery slower relative to its max capacity.
By taking a little extra care, you can go the extra mile – or a few thousand – on your electric scooter. Enjoy the ride!

8. Warning Signs: Spotting a Failing Electric Scooter Battery Before It’s Too Late
Every scooter rider dreams of endless, worry-free rides. However, like all things, your scooter’s battery has a life cycle. Knowing the signs of a failing battery can save you from unexpected hiccups during your ride.
One of the earliest red flags of a worn-out battery is the noticeable shortening of your scooter’s range. Over time, the cells in an aging battery become less efficient, causing a drop in capacity. When battery sag, or a temporary drop in performance, starts to occur, it’s time to pay attention.
You may also observe rapid drops in voltage when your battery’s capacity is below 30%. This can even lead to sudden shut-offs at around 20%. This is where your display or battery indicator can be misleading. It may show a state of charge that correlates with the voltage, but the true capacity of the battery is lower due to worn-out cells. Another sign is when your scooter takes a longer time to charge or if the charger indicates a full charge prematurely.
A battery management system (BMS) is a fail-safe designed to protect you and your battery. It monitors the battery pack and controls the charging and discharging process. If your BMS frequently cuts off power when the scooter is under load, it might be signalling that the battery needs replacing. Being aware of these warning signs can help you maintain your scooter better, ensuring you enjoy your rides for longer.
9. Preventing Electric Scooter Battery Fires: Safety Measures You Need to Know
Battery safety is key in electric scooters. But how can we prevent those scary electric scooter battery fires?
First, always use the right charger. Each battery needs a specific charger. Using the wrong one could overcharge the battery, causing it to overheat and catch fire.
Second, avoid extreme temperatures. Batteries don’t like being too hot or too cold. Always store your scooter in a cool, dry place.
Third, inspect your battery regularly. Look for any damage or signs of swelling. If you spot anything unusual, stop using the scooter immediately.
Fourth, never leave a charging battery unattended. Always be on hand to react quickly if something goes wrong.
Remember, electric scooter battery fires are rare. But by following these simple steps, you can reduce the risk even further. Safety should always be your top priority when enjoying your electric scooter.
Case Study
An e-bike store in lower Manhattan was recently the scene of a devastating fire, resulting in four fatalities. The fire’s cause was traced back to lithium-ion batteries used in e-bikes, according to the city’s Fire Commissioner, Laura Kavanagh. The location was familiar to the fire department, having previously received violations for related issues. Kavanagh warned about the extreme fire risk posed by these batteries, given the intense flames they produce when ignited. The store had faced previous inspection and fines for electrical wiring issues, battery charging practices, and the quantity of batteries present. Despite this, a planned reinspection had not yet taken place. In 2023 alone, New York City has witnessed 108 fires and 13 fatalities linked to lithium-ion batteries, leading to calls for stricter federal legislation regulating their safety standards.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, the battery of your electric scooter is more than just a power source—it’s the heart of your ride. Be it Lead-acid, Nickel-Metal Hydride, or the high-flying Li-ion, each battery type comes with its unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding terms like voltage sag, capacity rating, and C-rate can help you get the most out of your scooter’s battery life. Keep an eye on those telltale signs of a failing battery, practice safe charging habits, and remember that with the right care, you can significantly extend your battery life. Remember, knowledge is power. So arm yourself with these insights to enjoy a safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting scooter experience. Stay charged, stay safe, and enjoy the ride!


