Are Solar Batteries Worth It In Australia
Table of Contents
- Are Solar Batteries Worth It In Australia
- Why More Australians Are Turning to Solar Battery Storage
- What Solar Battery Storage Costs in Australia
- How Much Can You Save?
- Choosing the Right Solar Battery for Your Home
- Are Backup Batteries Worth the Investment?
- Virtual Power Plants and Smart Energy Use
- Off-Grid Living and Remote Setups
- Government Support and Financial Incentives for Solar Batteries
- When Will Solar Batteries Become More Affordable?
- Conclusion
- FAQ
- Hot Search
- Learn More About Battery
With electricity prices soaring across Australia, many households are searching for ways to take control of their energy bills and reduce reliance on the grid. Solar battery storage has become an increasingly popular solution as costs continue rising. This article is designed for Australian homeowners and renovators who are considering the benefits of solar battery storage. It will help you understand the practical advantages of installing a solar battery system, how to manage your energy use more effectively, and the government incentives available to make the switch more affordable. Whether you’re looking to invest in home storage batteries or seek more information, this guide will provide the insights you need to make a well-informed decision.
Why More Australians Are Turning to Solar Battery Storage
1. Tackling Soaring Energy Prices with Solar Power
Across Australia, households are facing some of the highest electricity prices in recent memory. With quarterly bills pushing past $500 in many regions, families actively seek more innovative, long-term solutions to manage their energy use. One of the fastest-growing options is installing rooftop solar with solar battery systems. This article is written for homeowners and renovators who want to understand whether investing in house battery storage makes sense today—and how it fits into Australia’s evolving energy future.
A solar battery allows you to store unused solar energy generated during daylight hours and use it later—especially during peak times when grid electricity costs the most. This shift in energy use offers not just cost savings but also added security during blackouts and better control over your household’s environmental impact.
2. How a Solar Battery Works Inside the Home
Here’s the basic setup: your solar panels absorb sunlight and generate electricity. Your home consumes what it needs immediately. The excess either gets exported to the grid or, if you have a solar battery, it gets stored for later use. Most Aussie homes without a battery only use about 25% of what their panels generate. You can increase that figure to 50% or more with a home storage battery.
This setup benefits those who use more power in the evening or work from home. A properly configured battery system can also charge during off-peak grid hours and discharge when rates spike. Some systems allow for emergency backup functions, keeping key circuits running during grid outages—ideal for households with essential medical equipment or families in blackout-prone regions.
Advanced systems include energy management tools that monitor and optimise real-time usage. Over time, this translates into better bill savings and more efficient use of clean power.
3. From Passive Consumption to Energy Independence
Australia leads the world in solar panel installations per capita. However, many homes still rely heavily on the grid due to limited home storage batteries. That’s starting to change. As feed-in tariffs decline and electricity rates climb, more households choose to hold onto their solar energy instead of selling it back for cents.
Installing a battery shifts your role from energy consumer to active energy manager. You decide when to store, when to use, and even when to export. With growing interest in electric vehicles and future technologies like vehicle-to-home (V2H) charging, a battery also sets the foundation for more flexible energy systems.
Government incentives in states like Victoria and South Australia are helping to offset the high cost of solar battery systems, making them more financially accessible. Combined with bright usage patterns and well-sized systems, many Australians are now reaching payback periods of 7 to 10 years, especially in regions with high peak tariffs.
What Solar Battery Storage Costs in Australia
Installing a solar battery offers long-term savings, but the upfront investment is no small feat. In this section, we’ll break down the full picture—from average system pricing to unexpected costs that often get overlooked. This guide is designed for Aussie homeowners trying to weigh the real financial commitment and potential return of adding house battery storage to their solar setup.
1. Average Cost for Solar Battery Systems in Australia
Across Australia, the average price for installing a solar battery is roughly AUD 2,325 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). That means for a 10kWh setup—common for mid-sized households—you’re looking at a price tag between AUD 20,150 and AUD 23,250, depending on brand, technology, and installer.
Here are a few examples of what you might pay for some of the better-known systems:
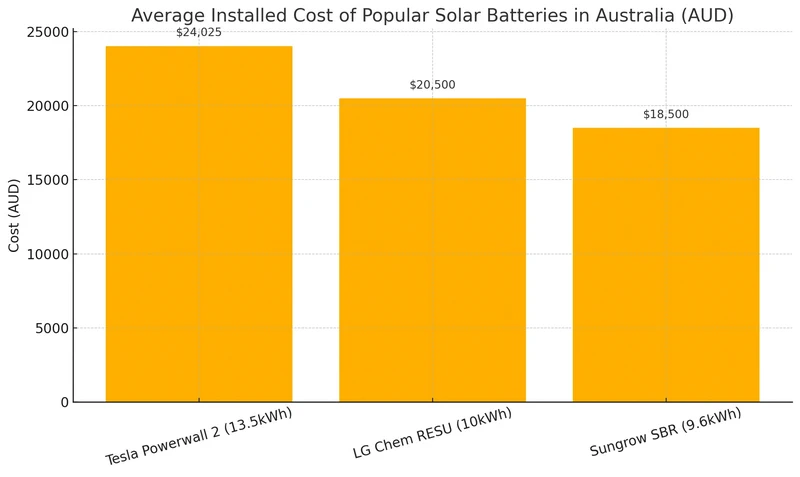
- Tesla Powerwall 2 (13.5kWh): Around AUD 24,025 installed
- LG Chem RESU 10kWh: Close to AUD 20,500
- Sungrow SBR Stackable System (9.6kWh): About AUD 17,000–AUD 19,500, depending on configuration
- MANLY 10KWH Battery (AUD 2,300) is another strong contender for Australian homeowners. This high-performance lithium iron phosphate battery comes with a 10-year warranty and offers excellent value for money, especially when compared to other premium models like the Tesla Powerwall. The MANLY 10KWH battery provides reliable solar energy storage with safety features such as overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuit protection. It’s ideal for those seeking a long-lasting and cost-effective solar battery solution.
While prices have been gradually dropping over the past few years, they’re still far from “budget-friendly” for most households—especially compared to the initial cost of rooftop solar panels.
2. Upfront vs Long-Term Costs: Understanding Payback Time
Solar battery storage costs aren’t just about what you pay on day one. The key is understanding your payback period—how long it’ll take for your energy savings to equal what you spent.
For most homes in Australia, that break-even point lands somewhere between 8 and 12 years, assuming you consume a good chunk of your energy during peak evening hours or use home storage batteries to dodge high feed-in tariff drops.
For example:
- A household in South Australia using 30kWh/day with time-of-use rates could shave AUD 1,400 to AUD 1,800 off yearly energy bills.
- That same home with a AUD 20,000 battery setup might recoup the investment in 10 to 12 years, especially if it optimises charging during off-peak and uses stored energy during peak.
- With a price of AUD 2,300 for the MANLY 10KWH Battery, this system offers a more affordable entry point for homeowners looking to invest in solar storage. The system’s long lifespan, with over 6,000 cycles, and the potential to recoup your investment in 8 to 12 years, makes it a great option for reducing energy bills while ensuring a safe, reliable energy solution.
Remember that battery warranties typically run for 10 years or about 6,000 charge cycles. Timing your return around that lifespan is essential if your goal is financial savings rather than backup security.
3. The Hidden Costs: Installation, Maintenance and Upgrades
Beyond the sticker price of the battery itself, there are plenty of hidden costs that buyers often overlook.
Installation & Setup:
Depending on your solar configuration, installation may involve extra wiring, switchboards, and mounting infrastructure. Expect to pay an additional AUD 1,550–AUD 4,650 for this work, primarily if your current inverter doesn’t support hybrid storage.
Hybrid Inverter Upgrade:
If your inverter isn’t compatible with a battery, you may need to upgrade to a hybrid inverter, which will add another AUD 3,100–AUD 4,650 to your bill.
Ongoing Maintenance:
While home storage batteries like lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) require minimal upkeep, periodic system checks are still necessary to keep warranties valid and avoid performance drops. Some installers include this in the price, but others charge annual servicing fees.
Smart Monitoring Apps & Grid Integration:
You’ll want a system that integrates with innovative energy tools, tracks usage, and schedules charging during off-peak hours to get the most from your battery. These extras are sometimes bundled, but not always—so double-check what’s included.
How Much Can You Save?
Understanding how much you can save with a solar battery depends on several key factors: how your household uses electricity, what tariffs apply in your area, and how well your system is designed. While a house battery storage system can dramatically cut your power bills, it doesn’t always translate into fast financial payback. Let’s unpack the real numbers and stories across Australia.
1. Comparing Homes with Just Solar Panels vs Solar Battery Systems
If your home only uses solar panels, you’re likely consuming about 20–30% of the energy your system generates. That’s because peak solar generation usually happens during the day while most people are away. In contrast, a home with a solar battery can use around 60% or more of its generated electricity by storing and reusing it later, particularly during peak-rate evenings.
But does doubling your self-consumption automatically mean doubling your savings?
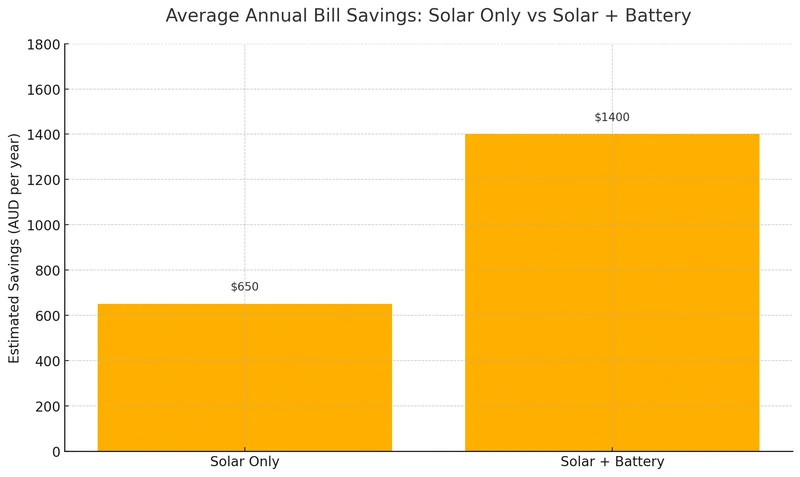
Not quite. The cost for solar battery installation is still relatively high in Australia, averaging between $1,400 and $1,800 per kWh installed. That means a 10kWh home storage battery system could cost between $14,000 and $18,000. While this might bring quarterly bills down from $800 to under $50, as seen in real cases, your break-even point could still take anywhere from 7 to 13 years, depending on your usage, incentives, and feed-in tariffs.
Here’s a visual breakdown:
| System Setup | Avg Upfront Cost (AUD) | Avg Annual Bill Savings | Estimated Payback Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar panels only | $5,000–$9,000 | $800–$1,500 | 3–5 years |
| Solar + 10kWh battery | $15,000–$20,000 | $1,400–$2,000 | 8–12 years |
| Solar + battery + TOU | Varies (same range) | Up to $2,500 | 6–10 years (with optimisation) |
2. Factors Affecting Savings: Usage Patterns, Feed-in Tariffs, and Location
No two households are the same. Your potential savings depend heavily on your electricity habits and local pricing.
Here’s what makes a difference:
- Usage patterns: Households that run high-draw appliances like dishwashers, A/C, and washing machines during the day can rely more on solar energy and charge their batteries efficiently. Families that use more power after sunset benefit most from home storage batteries.
- Time-of-use (TOU) plans: Switching to a TOU tariff allows you to charge your battery during low-cost overnight periods and use that stored power during expensive peak hours. In SA, for instance, off-peak power can be as low as 8c/kWh, while peak can hit 54c/kWh.
- Feed-in tariffs (FiT): As FiTs keep dropping—some falling below 5c/kWh—it’s becoming more profitable to store and use your power than sell it back to the grid.
- Location & sunlight: Sunshine hours vary widely across Australia. Perth and Brisbane homeowners tend to achieve faster battery ROI due to higher solar generation. Melbourne and Hobart may need larger systems or smarter energy-shifting to reach the same payback.
Here’s an illustration from a South Australian user:
“I charge the battery off the grid at 8c overnight and avoid using grid power during the 54c peak. My average kWh cost is just 11c now.”
These strategic usage models don’t just cut bills—they shorten payback periods, sometimes by 2–3 years.
3. Real-World Case Studies Across Different Australian States
Across forums and research studies, Aussie homeowners have shared how house battery storage works in the real world:
- Western Australia: A Perth user installed a 13.5kWh Tesla Powerwall with a 13kW solar system. Despite an $18,000 outlay, they cut their bills from $800 per quarter to $26. The payback period? Around 6–7 years—even quicker if electricity prices rise further.
- Victoria: In regional areas like North Central Vic, retirees with a modest solar battery setup saw minimal financial savings but huge lifestyle benefits. During a 30-hour blackout, their battery-powered essentials—medical fridges, lights, and phone chargers—kept their household and neighbours safe.
- Queensland: A North QLD family with an extensive system (13kW solar, no battery) finds their summer bills hover around $100, and they expect $0 bills in winter. Yet they admit a battery would only pay off if they upscaled the system significantly.
- South Australia: A user with a battery and EV shifted usage to off-peak hours, charging their battery overnight at 8c and avoiding peak tariffs altogether. Their monthly bill dropped from $300 to just $40.
The common takeaway? Financial outcomes vary, but for high-consumption homes, households working from home, or those with regular outages, a solar battery often delivers more than just cost savings—it delivers resilience and peace of mind.
Choosing the Right Solar Battery for Your Home
When selecting a solar battery for your home, it’s essential to ensure that the system matches your energy needs and budget. Understanding the right size and type of home storage batteries can help you save money in the long run and make the most of your solar investment. This section will guide you through the key considerations to ensure that you choose the right battery system for your lifestyle and energy requirements.
1. Sizing Your System Based on Daily Energy Use
To find the correct solar battery for your home, you must evaluate how much energy your household consumes daily. This is often referred to as your daily load. A smaller battery might suffice if your household uses much energy during the day and can rely on solar energy while the sun shines. However, if you use more energy during the evening, you’ll need a large battery to store energy produced during the day for later use. If you’re looking for a battery system that balances affordability and performance, the MANLY 10KWH Battery (AUD 2,300) is a great choice. It provides enough capacity for mid-sized households while remaining cost-effective, and its modular design allows for expansion, making it suitable for those who may want to scale up their energy storage in the future.
For example, a typical Australian household that uses around 20-30 kWh daily will benefit from a solar battery in the 10kWh to 15kWh range. Smaller homes or those with fewer energy needs may only need a 6kWh battery. Remember that the size of your solar panel system is also an essential factor when choosing your battery size. A more extensive solar panel system with a higher capacity will require a bigger battery to store excess energy.
In addition, understanding your energy consumption patterns can help optimise your system. If you’re often out during the day or have energy-intensive appliances that run at night, a larger home storage battery will help ensure you’re not drawing from the grid during peak times.
2. Avoiding Over-Investment: What Size Fits Your Lifestyle?
While opting for the largest solar battery available may be tempting, this could lead to unnecessary costs. Bigger batteries come with higher upfront costs; not all homes need large storage capacities. A smaller, more affordable system may meet your needs if you use less energy or shift some of your consumption to daytime hours when your solar panels generate energy.
A solar battery in the 6kWh to 10kWh range will be sufficient for most households. It’s crucial to balance capacity with usage. A 10kWh battery can store enough energy for a typical household to cover evening energy use, but over-investing in a 15kWh system may result in unnecessary storage capacity that you won’t use frequently.
When choosing your battery size, consider your lifestyle and future needs. If you’re planning on installing electric vehicle chargers or upgrading major appliances, you may need to invest in a slightly larger home storage battery to accommodate these changes.
3. Questions to Ask Your Installer Before You Buy
Before installing a solar battery system, ask your installer several questions to ensure the system is right for your home. First, ask about the warranty on the solar battery. Most reputable systems, especially lithium-ion batteries, come with 10 years or more warranties. This guarantees the battery’s performance over a significant period.
Second, inquire about the lifespan and charging cycles of the home storage batteries. A typical lithium battery can last up to 4,000 charge cycles, translating to approximately 10 years of use. Understanding this will help you estimate how long your battery will serve you before requiring a replacement.
Another critical question is whether the system is designed for backup power in case of grid failure. Some systems can function as backup generators during power outages, which can be crucial in areas prone to disruptions. Be sure to clarify this with your installer and check if additional components are required for this function.
Ask your installer for an energy assessment based on your home’s needs. They should provide recommendations tailored to your energy consumption, the size of your solar panel system, and your desired savings. They should also outline installation costs and potential additional work, such as wiring or system upgrades.
Are Backup Batteries Worth the Investment?
Backup batteries are becoming more popular for homeowners who want to ensure an uninterrupted power supply, especially in the face of rising electricity costs and frequent power outages. But are they worth the investment? The answer largely depends on your needs, location, and how much you rely on electricity daily. This section will explore the advantages of having a backup battery, its role in providing blackout protection, and how it compares to other backup solutions like generators.
1. Blackout Protection and the Value of Uninterrupted Electricity
In Australia, frequent blackouts and power disruptions can pose significant challenges, especially during severe weather events or high-demand periods. For homeowners who rely on electricity for critical appliances—such as medical equipment, refrigeration, or home offices—a backup battery provides a valuable line of defence. By storing solar energy or charging during off-peak hours, these batteries ensure you can continue using essential services when the grid is down.
The key benefit of a solar battery is its ability to deliver uninterrupted power when needed most. Unlike generators requiring fuel and maintenance, home storage batteries offer a cleaner, more efficient solution. Depending on the battery’s capacity and energy needs, a backup battery can power your home for several hours or even days without needing external energy sources.
2. Battery vs Generator: Cost and Reliability in Emergencies
When comparing backup power options, batteries and generators are the two most common choices, but they each have pros and cons.
- Backup batteries, particularly lithium-ion types, are more reliable in the long run. They have a longer lifespan, require less maintenance, and operate silently. Once installed, they don’t need fuel to generate power—making them a more sustainable and eco-friendly option.
- While initially cheaper to purchase, generators come with ongoing fuel and maintenance costs. They are also noisy and can emit harmful pollutants, making them less desirable for long-term use. Additionally, the cost of running a generator can add up quickly, especially during power outages that last for hours or days.
Regarding emergency use, a solar battery is a more efficient option, especially if you have a solar panel system installed. By storing excess solar energy, you can reduce your reliance on the grid, cutting costs and increasing energy independence. Although generators might seem more cost-effective upfront, the hidden fuel, maintenance, and environmental impact costs can make them a less favourable choice over time.
3. Backup Functionality: What Your Battery System Needs to Include
Not all home storage batteries are designed to handle the same power demands. When choosing a backup battery for your home, it is essential to ensure that the system is tailored to your specific needs.
- Battery Capacity and Size: The size of your solar battery should match your household’s energy consumption patterns. If you live in a large home or have high energy needs, you’ll require a larger capacity battery. For example, a 10kWh battery may be sufficient for smaller homes, while larger homes or those with electric vehicles may need a 20kWh battery or more.
- Inverter Compatibility: The inverter converts the stored energy in your battery into usable power for your home. Ensure that your battery system is compatible with your existing inverter or that the installer can provide a suitable inverter for optimal performance.
- Innovative Technology and Monitoring: Many solar battery systems now have innovative technology that allows you to monitor energy usage and battery performance remotely. This feature lets you track how much power you are storing, when to charge your battery, and whether any issues need addressing.
- Grid Connection and Backup Power: While most solar batteries can store energy during non-sunny periods, some systems are designed to continue operating even when the grid is down. If blackout protection is a priority, select a battery system that includes this feature, ensuring you have reliable backup power during outages.
Virtual Power Plants and Smart Energy Use
1. Understanding Virtual Power Plants (VPP) and Their Function
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is a network that connects multiple home storage batteries and solar energy systems to work together like a single power plant. Instead of relying on a traditional power station, a VPP gathers excess energy generated by solar panels in homes and stores it in solar batteries. This energy can then be released back into the grid when needed, especially during high-demand periods.
Through advanced energy management systems, homes with solar panels and batteries can act as part of a more extensive network, sharing their stored energy and contributing to a more stable and sustainable energy supply. VPPs help balance energy supply and demand, allowing homes to sell excess power back to the grid, making the most out of solar energy and reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
2. Why Joining a VPP in Your Neighbourhood Makes Sense
Becoming part of a Virtual Power Plant can offer numerous advantages to homeowners and the broader community.
Financial Rewards
When you participate in a VPP, you can earn money by sharing the energy stored in your solar battery with the grid. During periods of high energy demand, your stored energy can be used, and you receive compensation in return. This system helps reduce overall energy costs for the community while rewarding individuals for contributing to the grid.
Strengthening the Grid
VPPs enhance grid stability. By enabling a decentralised energy storage and distribution approach, VPPs help prevent blackouts and ensure there is always enough energy during peak usage times. This shared approach is more reliable and sustainable than traditional power generation methods.
Supporting Clean Energy
By joining a VPP, homeowners can actively contribute to the clean energy transition. The collective storage and distribution of solar energy across multiple homes reduce dependence on fossil fuels and support the shift towards renewable energy sources.
Lower Energy Bills
Participating in a VPP can help reduce energy bills. Not only do you earn money by sharing your stored energy, but you can also reduce your reliance on grid power, particularly when electricity prices are high. This makes VPPs a smart way to optimise energy use and costs.
3. Using Smart Systems and Timers to Cut Back on Battery Needs
While having a home storage battery is beneficial, it’s not always necessary for every household. Intelligent energy systems and timers can help you maximise solar energy without needing large batteries.
Timed Energy Consumption
Appliances like washing machines and water heaters can be programmed to run during daylight hours when your solar system is generating the most energy. By using these appliances when energy production is high, you can reduce your reliance on home storage batteries and maximise your solar power.
Smart Home Energy Management
Intelligent energy management systems automatically adjust how and when your appliances use energy. These systems can help schedule energy-intensive activities like running the dishwasher or cooling the home during the day, optimising the use of available solar power. As a result, you’ll need fewer solar batteries, saving on installation and maintenance costs.
3Lower Energy Costs
By relying on timers and intelligent energy systems, households can maximise the use of their solar generation, reducing energy bills without needing larger battery storage. In areas with high solar production, shifting appliance use to peak solar hours can significantly reduce energy costs.
Off-Grid Living and Remote Setups
1. The Necessity of House Battery Storage for Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid requires a sustainable energy solution, and house battery storage is essential to the equation. Without access to the electrical grid, energy must be produced and stored on-site, and solar batteries are the most effective option for maintaining a constant power supply.
Energy Security
For off-grid homes, solar energy storage ensures that power is always available, even during cloudy days or at night. This means you can generate, store, and use your energy independently of the grid, making it perfect for remote areas.
Reducing Generator Dependence
Off-grid homes have relied on diesel generators as a backup power source for years. However, solar batteries eliminate the need for these fuel-dependent systems. With a solar battery, homes can rely on clean, renewable energy without the ongoing fuel cost.
2. Sizing Batteries for Cabins, RVs, and Remote Properties
Proper sizing is crucial when planning for battery storage in remote or mobile setups. The size of your solar battery depends on the energy you use daily and the space available for storage.
Energy Consumption
For a small cabin or RV, a 3-4 kWh solar battery might be enough to cover basic needs. Larger properties or homes that use more energy-intensive devices like air conditioning or heating systems will require larger batteries to ensure enough stored power is available during high-demand times.
Battery Sizing Considerations
It’s essential to factor in your peak energy consumption, particularly during high usage periods. For example, a home with multiple residents or one that requires air conditioning will need a larger battery setup. Battery sizing should be based on typical daily use, and extra capacity should be considered for backup during low sunlight periods.
3. Backup Options for Rural and Mobile Use
While solar batteries are the best solution for most off-grid homes, other alternatives are worth considering, particularly for mobile or rural setups.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators can provide a reliable backup power source for more significant remote properties or mobile setups like RVs. However, they come with the environmental cost of fossil fuel and the expense of ongoing fuel purchases. Diesel generators should be a secondary option rather than a primary energy source.
Hybrid Energy Systems
A hybrid system that combines solar energy, solar batteries, and generators can provide flexibility and security in remote locations. This setup ensures you have power regardless of weather conditions or energy consumption, but it may involve higher initial costs.
Wind and Hydroelectric Power
In certain areas, wind turbines or small-scale hydroelectric systems can be added to the mix, allowing for continuous energy generation even when solar energy is low. These systems can complement home storage batteries, providing a more reliable off-grid power solution.
In conclusion, whether you want to optimise your solar energy storage or set up a robust off-grid system, proper planning and technology will ensure you maintain a reliable and cost-effective power supply. It’s possible to live off the grid sustainably and efficiently through Virtual Power Plants, smart energy systems, or by choosing the right battery size for your needs.
Government Support and Financial Incentives for Solar Batteries
1. Available Solar Battery Rebates and Interest-Free Loans
In Australia, government incentives play a significant role in making solar battery storage more accessible to homeowners. State and federal programs offer substantial solar battery rebates and interest-free loans to help reduce the upfront costs of installing home storage batteries. These initiatives aim to make it easier for households to store excess solar energy and become less reliant on the grid.
For instance, Solar Victoria offers rebates and interest-free loans for eligible residents who want to add solar batteries to their existing rooftop solar systems. These financial incentives significantly lower the installation costs and encourage the uptake of clean energy solutions. Similarly, in Queensland, the government provides solar battery rebates, making it more affordable for residents to install solar storage systems as part of their renewable energy transition.
These programs are instrumental in helping Australians reduce their energy bills, increase energy independence, and contribute to the nation’s renewable energy targets. By taking advantage of these financial supports, households can achieve quicker payback periods and enjoy more significant long-term savings on their electricity costs.
2. State-Specific Programs and Their Eligibility Criteria
Different Australian states offer unique programs that support the installation of solar batteries. Each state has its eligibility requirements, meaning that the availability of incentives can vary depending on your location. For example, Solar Victoria provides financial assistance through rebates and interest-free loans to Victorian residents who have already installed solar panels and wish to add battery storage.
In New South Wales, the government offers rebates and support for solar battery systems, with a specific focus on reducing emissions and increasing renewable energy usage across the state. South Australia also offers targeted incentives for home storage batteries as part of its clean energy policy.
Before applying for a rebate or loan, you must check the eligibility criteria for your state’s program. Requirements typically include household income, system size, and whether the installation is for an existing or new system. Understanding these details ensures you can fully utilise the available financial support.
3. What to Expect in Future Policy Changes
Australian government policies will likely continue evolving to support renewable energy adoption, including solar battery storage. As more households install solar panels and incorporate battery storage into their energy systems, financial support for these systems is anticipated to expand.
Future policy changes may include further incentives for those participating in Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), where households with solar batteries share their stored energy with the grid. Participation in such programs can offer additional financial rewards while improving grid stability and encouraging a more sustainable energy system. Over time, these changes are expected to help reduce the cost of solar batteries, making them even more accessible to homeowners across Australia.
As electricity prices rise and environmental goals tighten, government incentives will likely increase in scope and value, making solar battery systems an even more attractive investment for Australian homes.
When Will Solar Batteries Become More Affordable?
1. Trends in Solar Battery Prices
Over the past few years, the price of solar batteries has dropped significantly, thanks to technological advances and increased competition within the market. The growing demand for home storage batteries has encouraged more manufacturers to enter the market, leading to lower prices. The widespread adoption of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, known for their safety and long lifespan, has also contributed to reducing the overall cost of solar storage systems.
Currently, solar battery storage costs approximately $1,500 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). However, as production increases and battery technology improves, prices are expected to fall even further over the next few years. This will make solar batteries a more affordable option for Australian households, offering more significant savings on energy bills and reducing dependence on the grid.
While the cost of solar batteries will vary depending on factors such as the size of the system and the brand, the overall trend points towards a more affordable future, with solar battery storage becoming increasingly accessible to more Australians.
2. Technology Improvements and Mass Production Effects
As production capacity grows and battery technology continues to improve, the cost of solar batteries is expected to decrease significantly. With increased competition and the refinement of existing technologies, such as solid-state batteries and more efficient lithium-ion options, the overall price of solar storage systems will continue to fall.
The mass production of solar batteries is also a key factor contributing to lower prices. As more units are produced, economies of scale will reduce manufacturing costs, reducing the price of each unit. Solar batteries will become even more affordable for homeowners, making them a more practical and attractive solution for energy storage in the coming years.
With these technological advancements, solar batteries are expected to become more reliable, efficient, and cost-effective, paving the way for widespread adoption.
3. Should You Wait or Buy Now?
Whether it’s better to buy a solar battery system now or wait for prices to drop further depends on your specific needs. Installing a solar battery system can reduce your energy bills immediately. In addition, government rebates and interest-free loans are currently available, helping offset the high initial installation cost.
However, if you are focused on long-term savings and don’t need solar battery storage, it might be worth waiting for prices to fall further. As solar batteries become more affordable over time, you can access better options at lower prices and with improved technology.
The decision to buy a solar battery now or later depends on factors such as your energy usage, budget, and whether you want to lock in current government support while prices remain favourable. If you’re eager to switch to renewable energy and take advantage of the existing financial incentives, now may be the right time to invest in solar battery storage. However, if you’re willing to wait, you can expect even better options at lower prices shortly.
Conclusion
As electricity costs continue to rise, solar battery storage offers Australians a practical and cost-effective way to manage their energy needs. With technological advancements driving down prices and the added benefit of government incentives, solar battery systems are becoming an increasingly attractive investment. For households looking to reduce their energy bills and increase energy independence, investing in home storage batteries can provide long-term savings and help contribute to a more sustainable future. As solar battery technology becomes more affordable and accessible, there’s never been a better time for Australian homeowners to consider this energy-saving solution. By making the switch, you take control of your energy costs and play a part in Australia’s clean energy transition.
FAQ
1. How long does a 5kW solar battery last?
A 5kW solar battery typically lasts for 10-15 years, depending on several factors, such as the battery type, usage, and maintenance. In general, lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used for solar storage, offer a lifespan of 5,000 to 6,000 charge cycles. This translates to around 10-15 years if you follow optimal charging practices. Regular maintenance, such as checking the battery’s health and ensuring it is not exposed to extreme temperatures, can help extend its lifespan. How the battery is used and how often it’s charged and discharged will also impact how long it lasts.
2. What happens when off-grid solar batteries are full?
When off-grid solar batteries are full, the system’s built-in charge controller will prevent the battery from overcharging. Most modern solar battery systems have a Battery Management System (BMS) that automatically stops the battery from charging once it reaches its maximum capacity. In an off-grid setup, once the battery is full, any excess energy generated by the solar panels is either diverted to other uses (such as powering appliances) or redirected to a backup system, if available. Some systems also allow the excess energy to be fed into an alternative energy storage solution or even back to the grid if the system is grid-tied. The main goal is to ensure that the battery does not overcharge, which could damage the system and reduce its lifespan.






