How Long Do Lithium Batteries Last
Table of Contents
- How Long Do Lithium Batteries Last
- How to Calculate the Cycle Life of Lithium Batteries?
- Do Lithium Batteries Last Longer Than Other Batteries?
- Key Factors That Influence Lithium Battery Lifespan
- 5 Proven Ways to Extend Lithium Battery Lifespan
- Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Have a Memory?
- Do Lithium Batteries Expire If Not Used?
- Which Brand of Battery Lasts the Longest?
- Will Lithium Batteries Last for 6 Months?
- Conclusion
- FAQ
- Hot Search
- Learn More About Battery
Understanding the lithium battery lifespan is essential for maximizing the value and efficiency of modern energy solutions. As a key component in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics, lithium batteries offer a remarkable combination of longevity, energy density, and reliability. By maintaining proper care and following best practices, users can significantly extend the lithium battery life expectancy, ensuring consistent performance across various applications. This guide will explore essential factors influencing battery longevity and actionable steps to optimize usage.
How to Calculate the Cycle Life of Lithium Batteries?
Understanding the lithium battery lifespan is essential for optimizing its use and ensuring you get the most value out of it. The cycle life of a lithium battery refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles it can complete before its capacity significantly degrades.
1. Depth of Discharge (DoD)
The Depth of Discharge (DoD) measures how much of the battery’s capacity is used during each cycle. Batteries that operate at a lower DoD—such as 50%—tend to last longer, with higher total cycle counts, compared to those operating at a deeper DoD like 80% or 100%.
2. Manufacturer-Specified Cycles
Each battery is designed with a specific cycle lifespan, often provided by the manufacturer. These values are usually based on ideal operating conditions. For instance, some advanced lithium batteries offer between 10,000 and 15,000 cycles at 60% DoD, while others are designed for around 3,000 cycles at 80% DoD.
3. Daily Usage
The frequency of charging and discharging the battery plays a crucial role in its lifespan. A battery used for one full cycle per day will last significantly longer than one used for two or more cycles daily. For heavy users, this is a critical factor to consider when calculating overall longevity.
4. Environmental and Charging Conditions
Environmental factors such as temperature and charging habits also influence the lifespan of lithium batteries. High temperatures (>35°C or 95°F) and frequent fast charging can accelerate degradation, reducing the total number of usable cycles. On the other hand, maintaining moderate temperatures and following manufacturer-recommended charging practices can extend the battery’s life.
5. Incorporating Battery Age
Batteries naturally degrade over time, even when not in use. By factoring in how long the battery has already been used, our calculator adjusts its predictions to reflect the realistic remaining lifespan. This is especially important for batteries that have been in service for several years.
6. Using Our Lithium Battery Lifespan Calculator
Our calculator takes all these factors into account to provide an accurate estimate of your battery’s remaining lifespan. Simply input values such as DoD, manufacturer-specified cycles, daily usage, temperature, and charging habits to get a result tailored to your specific battery conditions.
Use the calculator below to discover how much longer your lithium battery can last under its current usage conditions:
Lithium Battery Lifespan Calculator
Do Lithium Batteries Last Longer Than Other Batteries?
Lithium batteries typically last much longer than other battery types, such as lead-acid or nickel-based batteries. Their advanced cycle life, high energy density, and low maintenance requirements make them a superior choice in many applications. Let’s delve into the data and practical comparisons.
1. Comparison of Lithium Batteries with Lead-Acid and Nickel-Based Alternatives
- Cycle Life
- Lithium batteries excel with 3,000 to 5,000 partial cycles, compared to lead-acid batteries’ 500-1,000 cycles and nickel-based batteries’ 1,000-1,500 cycles.
- For instance, a lithium battery used in an electric vehicle (EV) and charged daily can last over eight years. In contrast, a lead-acid battery might require replacement within two to three years under the same conditions.
- Energy Density
- The energy density of lithium batteries (110-250 Wh/kg) significantly surpasses that of lead-acid batteries (30-50 Wh/kg). This higher energy density means that lithium batteries are lighter and deliver longer runtimes, crucial for EVs, drones, and portable devices.
- Efficiency
- Lithium batteries offer 90-95% efficiency during charging and discharging, compared to 70-85% for lead-acid batteries. This makes them more cost-effective over time, reducing energy waste.
- Maintenance
- Lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, such as adding distilled water and checking for corrosion. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, are virtually maintenance-free, saving users both time and money.
2. Key Advantages of Lithium Battery Life Expectancy
- Long Lifespan: The average lithium battery lifespan is 8-10 years, significantly longer than the 2-3 years typical of lead-acid batteries.
- Low Self-Discharge: Lithium batteries self-discharge at a rate of only 1-3% per month, compared to 5-15% for lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for standby or backup applications.
- Environmental Benefits: While lead-acid batteries are recyclable, their short lifespan and hazardous components make them less eco-friendly compared to lithium batteries.
3. Real-World Examples
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Tesla’s EV batteries, manufactured by industry-leading battery brand Panasonic, are designed to retain 70-80% of their capacity even after 200,000 miles, highlighting their exceptional durability. - Solar Energy Systems
In residential solar systems, lithium batteries often outlast lead-acid batteries by 5-7 years, providing reliable energy storage and reducing the need for frequent replacements. - Marine Applications
Lithium batteries are increasingly popular in marine systems for their lightweight design and ability to deliver consistent power over extended periods, outperforming traditional lead-acid options.
4. Average Lifespan of Battery Types
| Battery Type | Average Lifespan (Years) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | 8-10 | 110-250 | 3,000-5,000 |
| Lead-Acid | 2-3 | 30-50 | 500-1,000 |
| Nickel-Based | 3-5 | 60-120 | 1,000-1,500 |
Key Factors That Influence Lithium Battery Lifespan
1. Temperature Effects on Longevity
Extreme temperatures significantly impact the lithium battery lifespan, making proper temperature management essential. High temperatures accelerate internal chemical reactions, leading to faster degradation, while low temperatures reduce capacity and increase resistance.
- High Temperatures: Operating a lithium battery above 35°C (95°F) can permanently reduce its capacity. For example, EV batteries exposed to constant heat often lose efficiency faster, shortening their lifespan.
- Low Temperatures: At sub-zero conditions, the performance of lithium batteries decreases, affecting devices like winter drones or solar backup systems. For instance, at -10°C (14°F), the capacity of a lithium battery can drop by up to 30%.
- Optimal Temperature Range: Most battery manufacturers recommend maintaining a lithium-ion battery temperature range between 20°C-30°C (68°F-86°F) for prolonged performance.
Action Tip: Protect batteries in extreme climates. For instance, use insulated cases in winter or avoid storing devices in hot car interiors during summer.
2. Proper Charging Practices
Effective charging habits can extend the lithium battery life expectancy. Overcharging, over-discharging, or using low-quality chargers can severely damage batteries.
- Avoid Overcharging and Over-Discharging: Overcharging increases pressure inside the battery, risking leaks or explosions. Over-discharging below safe voltage levels leads to irreversible capacity loss.
- Use High-Quality Chargers: Chargers recommended by reputable battery brands or battery suppliers ensure consistent voltage and current, reducing the risk of overheating or circuit damage. A BMS for lithium-ion battery (Battery Management System) also regulates safe charging and discharging.
- Real-Life Scenarios: Daily-use devices like smartphones benefit from maintaining a charge level between 20%-80%. Backup systems such as solar batteries should avoid rapid charge-discharge cycles to maximize their lifespan.
Action Tip: Always use chargers specified by the battery manufacturer, and avoid fast charging unless necessary to minimize long-term wear.
3. Storage Conditions
Proper storage is crucial for extending the lithium battery lifespan, especially during extended periods of inactivity.
- Correct State of Charge (SOC): Storing batteries at a 40%-60% charge level prevents chemical reactions that degrade capacity. Fully charged or discharged batteries degrade faster in storage.
- Cool and Dry Storage: Avoid exposing batteries to temperatures above 35°C (95°F) or high humidity, as this accelerates degradation. Instead, store them in a dry, climate-controlled area.
- Common Mistakes: Many users leave devices in hot cars or store them fully charged for months, unknowingly reducing their lifespan.
- Practical Application: Solar energy storage systems perform better when lithium batteries are properly stored, lasting several years longer than those stored in suboptimal conditions.
Action Tip: If storing a device for months, charge the battery to 50% and place it in a dry location at room temperature.
4. Understanding Cycle Life
Cycle life measures the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity drops below 80%. It’s a critical factor in the lithium battery lifespan.
- What is Cycle Life? A cycle begins when a battery is fully charged and discharged. Partial cycles, such as charging from 50% to 80%, count as part of a full cycle.
- Usage Patterns and Impact: High discharge rates or frequent cycling (e.g., deep discharges) can reduce cycle life. For example, a lithium battery powering a drone used daily may reach its limit faster than one in occasional use.
- Graph Representation: Below is a simplified comparison of cycle life for different battery types:
| Battery Type | Cycle Life (Full Cycles) | Cycle Life (Partial Cycles) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium | 3,000-5,000 | Up to 10,000 |
| Lead-Acid | 500-1,000 | Up to 1,500 |
| Nickel-Based | 1,000-1,500 | Up to 2,000 |
Action Tip: Avoid full discharge cycles whenever possible. Instead, use partial cycles (20%-80%) to prolong battery life.
5 Proven Ways to Extend Lithium Battery Lifespan
Proper care and maintenance can significantly extend the lithium battery lifespan, saving costs and enhancing reliability. Here are five proven strategies to maximize the lithium battery life expectancy.
1. Use Original Chargers
Using original chargers or those provided by professional battery manufacturers, such as MANLY Battery, ensures proper voltage and current regulation, minimizing the risk of overheating and capacity degradation. Low-quality chargers, on the other hand, often fail to deliver consistent power, leading to potential damage.
- Why Choose Certified Chargers:
Chargers from trusted battery manufacturers are specifically designed to meet the technical requirements of lithium batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longer lifespan.
Action Tip: Always opt for original chargers or those provided by reputable manufacturers like MANLY Battery to maintain the efficiency and longevity of your lithium battery.
2. Avoid High Temperatures
High temperatures are among the top causes of reduced lithium battery lifespan, as they accelerate internal chemical reactions that degrade capacity.
- The Impact of Heat:
Prolonged exposure to temperatures above 35°C (95°F) can cause irreversible damage to the battery’s electrolytes. For example, solar batteries placed in poorly ventilated areas often lose efficiency faster. - How to Protect Your Battery:
Use insulated cases for outdoor equipment or ensure adequate ventilation for stationary batteries like those in RVs or boats.
Action Tip: Always keep your lithium battery within its recommended operating temperature range, typically 20°C-30°C (68°F-86°F), as specified by most battery brands.
3. Partial Charging and Discharging
Maintaining the battery charge level between 20% and 80% significantly extends its life. Full discharges and complete charges put unnecessary stress on the battery cells.
- Benefits of Partial Charging:
Partial cycles are less demanding on the battery, reducing wear and extending its lithium battery lifespan. - Common Misunderstanding:
Many users believe fully charging or discharging their batteries maximizes capacity. In reality, this accelerates degradation.
Action Tip: Monitor your battery’s charge level with a reliable Battery Management System (BMS for lithium-ion battery) to avoid extremes.
4. Reduce Fast Charging/Discharging
While fast charging is convenient, it generates excess heat and stresses the battery, shortening its lifespan.
- Risks of Rapid Charging:
Rapid charge-discharge cycles can cause thermal runaway, a condition where the battery overheats and damages internal components. This is especially problematic in high-drain devices like drones or smartphones. - Alternative Approach:
Use standard charging rates and avoid frequent high-load discharges unless absolutely necessary.
Action Tip: Opt for chargers that match the battery’s specifications to balance speed and long-term performance.
5. Proper Long-Term Storage
Proper storage practices are critical for preserving the lithium battery life expectancy, especially during periods of inactivity.
- Storage Best Practices:
- Charge the battery to 40%-60% before storing.
- Keep it in a cool, dry location with minimal humidity.
- Avoid storing batteries fully charged or completely discharged, as both extremes can degrade capacity.
- Seasonal Equipment Examples:
For RVs or boats used seasonally, ensure batteries are stored in climate-controlled areas to maintain their performance.
Action Tip: Regularly check stored batteries every 3-6 months to ensure they maintain an optimal charge level.
Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Have a Memory?
Lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect. Unlike older battery technologies such as nickel-cadmium (NiCd) or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), which suffer from this issue, lithium batteries are engineered to avoid the structural changes that lead to memory problems.
1. Explanation of Memory Effect
The memory effect refers to a phenomenon where batteries lose their full charge capacity if they are repeatedly charged and discharged only partially. This issue is particularly common in NiCd batteries. For example, if a NiCd battery is consistently recharged when it has only been 50% discharged, it can “remember” this partial cycle and fail to utilize its full capacity in subsequent uses.
In NiCd batteries, the memory effect occurs due to structural changes in the battery’s active materials during incomplete charge cycles. Over time, these changes prevent the battery from fully charging or discharging, reducing its effective capacity.
2. Why Lithium-Ion Batteries Are Unaffected
Lithium-ion batteries are not affected by the memory effect due to their unique chemistry and design. Here’s why:
- Electrode Materials:
- Lithium-ion batteries use materials like graphite (anode) and metal oxides (cathode), which do not undergo structural changes during charge and discharge cycles. This ensures consistent performance even with partial charging.
- Electrochemical Reactions:
- The charge-discharge process in lithium-ion batteries relies on the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes rather than material changes. This eliminates the risk of capacity loss due to incomplete cycles.
- Advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS):
- Modern lithium batteries are equipped with a BMS for lithium-ion batteries, which regulates voltage and current to prevent overcharging or over-discharging, further enhancing their reliability.
Do Lithium Batteries Expire If Not Used?
Lithium batteries can degrade over time, even if they are not used. While their shelf life is longer than most other battery types, inactivity and improper storage can negatively affect their chemistry and reduce their capacity.
1. Shelf Life of Lithium Batteries
The typical shelf life of a lithium battery is 2-5 years, depending on factors such as storage conditions and the quality of the battery. High-quality batteries from reputable battery manufacturers tend to last longer.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate:
Unlike older battery technologies, lithium batteries have a low self-discharge rate, typically around 1-3% per month. This allows them to retain most of their charge even after months of inactivity. - Chemical Degradation:
Over time, the electrolyte and electrode materials in the battery degrade, reducing capacity. This process occurs regardless of usage but accelerates under poor storage conditions.
2. How Inactivity Affects Battery Chemistry
When a lithium battery is not used for an extended period, several factors can contribute to its degradation:
- Voltage Drop:
- If a battery’s charge level drops below a critical threshold, the electrolyte can become unstable, permanently reducing capacity.
- Temperature Extremes:
- Storing batteries in high heat or freezing temperatures accelerates chemical reactions that degrade the battery.
- Full Charge or Discharge:
- Storing a battery fully charged or completely discharged can cause internal stress and reduce its lifespan.
3. Best Practices for Long-Term Storage
- Charge Level:
Store lithium batteries at around 40%-60% charge to minimize internal stress. - Environment:
Keep the battery in a cool, dry location with temperatures between 15°C-25°C (59°F-77°F). - Periodic Checks:
If the battery will be stored for several months, check and recharge it to the recommended level every 3-6 months to prevent deep discharge.
4. Impact of Storage Conditions on Lithium Battery Lifespan:
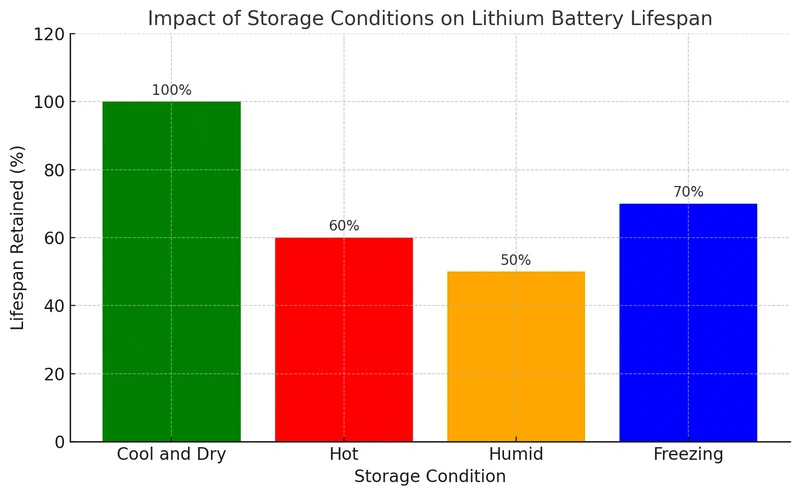
Which Brand of Battery Lasts the Longest?
When it comes to lithium battery lifespan, the brand plays a critical role in determining quality and durability. Renowned battery brands like Duracell, Energizer, Tesla, CATL, and MANLY Battery consistently lead the industry with their superior performance and longevity.
1. Overview of Top Brands
- Tesla:
Tesla is a leader in lithium-ion battery technology, particularly for electric vehicles (EVs). Their batteries, built with advanced cell chemistry and robust management systems, are engineered to last over 300,000 miles with minimal degradation. - CATL:
CATL is one of the largest global suppliers of lithium batteries, providing high-performance solutions for EVs, renewable energy systems, and industrial applications. Their batteries are renowned for their extended cycle life and energy efficiency. - MANLY Battery:
A leading Chinese battery manufacturer, MANLY Battery offers customizable lithium-ion solutions tailored to diverse applications, from solar energy storage to golf carts. With a 10-year warranty, advanced safety features, and global certifications (UN38.3, IEC62133, UL, CE), MANLY’s batteries set benchmarks for durability and efficiency.
2. What Sets Premium Batteries Apart?
- Cell Design:
High-quality batteries use advanced materials like LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate), which offer better thermal stability, longer cycle life, and safer operation compared to traditional lithium-ion chemistries. - Quality Assurance:
Premium battery brands rigorously test their products to ensure performance under extreme conditions, from high temperatures to deep discharges. - Battery Management Systems (BMS):
Reputable brands integrate advanced BMS for lithium-ion batteries, ensuring optimal charging, discharging, and temperature regulation to prolong battery life.
Will Lithium Batteries Last for 6 Months?
Lithium batteries can last for six months of inactivity if stored properly. While their low self-discharge rate helps maintain charge, improper storage conditions can degrade the battery and reduce its capacity.
1. Realistic Expectations for Short-Term Storage
- Low Self-Discharge Rate:
Lithium batteries typically lose only 1-3% of their charge per month when stored in ideal conditions, such as a cool and dry environment. Over six months, a high-quality battery will retain most of its charge. - Risks of Inactivity:
If a battery is stored fully discharged, it risks entering a deep discharge state, which can damage internal components and permanently reduce capacity.
2. Best Practices for Six-Month Storage
- Charge Level:
Store batteries at a 40-60% charge level to reduce internal stress. Fully charged or completely discharged batteries are more prone to degradation. - Environment:
Keep batteries in a dry location with a stable temperature between 15°C and 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Avoid storing them in humid or extremely hot environments. - Periodic Maintenance:
Check the battery’s charge level every three months. If the charge falls below 30%, recharge it to the recommended level.
Conclusion
The lithium battery lifespan depends on a variety of factors, including discharge depth, environmental conditions, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. By understanding and implementing best practices, users can maximize the lithium battery life expectancy, ensuring efficient energy utilization and cost savings over time. Whether for personal devices, electric vehicles, or energy storage, a well-maintained lithium battery delivers reliable performance and extended usability, making it a cornerstone of modern energy technology.
FAQ
1. Do lithium batteries really last 10 years?
Yes, lithium batteries can last up to 10 years, depending on the quality of the battery, usage patterns, and environmental factors. High-quality lithium batteries, such as those from reputable battery manufacturers, are designed to endure 2,000 to 5,000 cycles or more. With moderate usage and proper care, achieving a decade-long lifespan is possible.
2. Do lithium batteries last longer than regular batteries?
Yes, lithium batteries generally last longer than traditional batteries like lead-acid or nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries. Their superior lithium battery lifespan is due to their higher energy density, lower self-discharge rate, and longer cycle life. For example, a lithium battery can last up to 5,000 cycles, while a lead-acid battery typically lasts only 500-1,000 cycles.
3. How long do lithium batteries hold a charge?
Lithium batteries can hold a charge for several months when not in use, thanks to their low self-discharge rate of around 2-3% per month. This makes them ideal for applications like backup power systems and seasonal equipment. However, factors like storage temperature and battery health may affect performance.
4. Do lithium batteries get weaker over time?
Yes, lithium batteries gradually lose capacity over time due to natural aging and usage. This process is influenced by factors such as charging habits, discharge depth, and operating temperatures. On average, most lithium batteries retain 80% of their capacity after 500-1,000 cycles, but capacity diminishes with extended use.
5. Is it okay to leave a lithium-ion battery on the charger overnight?
It is generally safe to leave a lithium-ion battery on the charger overnight if it uses a high-quality charger with built-in overcharge protection. However, for optimal lithium battery life expectancy, it’s recommended to unplug the charger once the battery reaches full charge. Prolonged charging can generate heat, which may degrade the battery over time.










